FIG. 4.
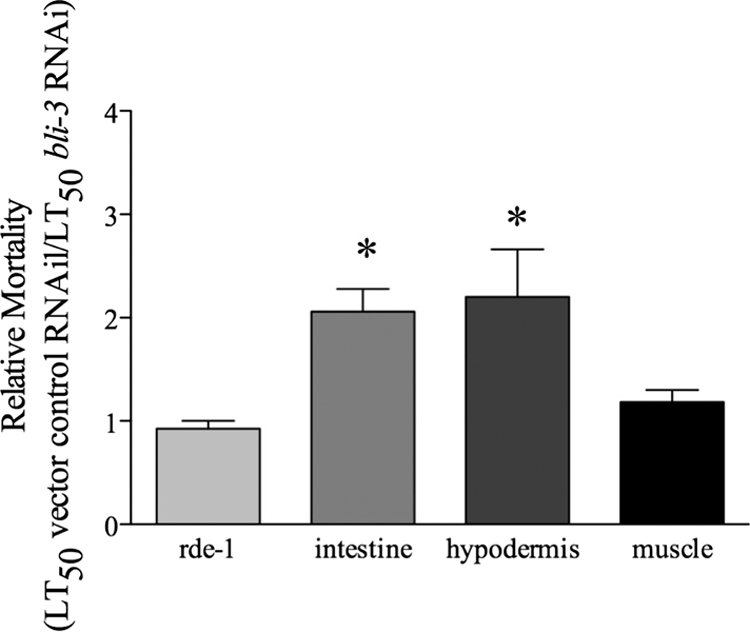
Reduction of bli-3 expression in the intestine and hypodermis increases susceptibility to infection. Reducing expression of bli-3 by RNAi in the intestine and the hypodermis, but not in the muscle, caused a significant increase in relative mortality. To determine relative mortality, the average LT50 on E. faecalis for each rde-1 strain previously exposed to vector control RNAi was divided by the LT50 for the same strain exposed to bli-3 RNAi. The averages from three independent experiments are shown. The error bars correspond to the standard errors, and asterisks indicate significant differences between the tissue-specific strain and the control strain (lacking rde-1 in all tissue) (P = 0.0019 [intestine], P = 0.0020 [hypodermis], and P = 0.3646 [muscle]).
