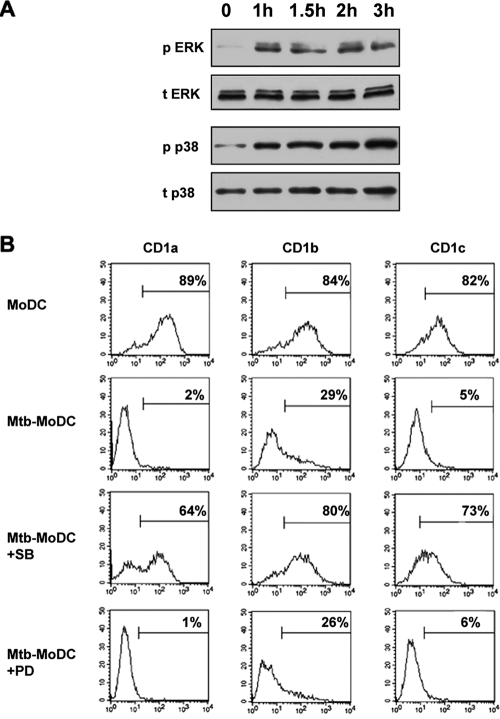
FIG. 1.
Mycobacterial infection of human monocytes causes their differentiation into CD1− DC by triggering p38 phosphorylation. (A) Monocytes were incubated with M. tuberculosis for the indicated times and treated as described in Materials and Methods to detect total ERK (t ERK), phosphorylated ERK (p ERK), total p38 (t p38), and phosphorylated p38 (p p38). Similar data were obtained in three independent experiments. (B) Monocytes were infected with M. tuberculosis and cultured with GM-CSF and IL-4 (Mtb-MoDC) for 5 days. Some of the monocytes were pretreated with the p38 inhibitor SB203580 (Mtb-MoDC+SB) or the ERK inhibitor PD98059 (Mtb-MoDC+PD) before infection. The markers excluded 95% of the events recorded with the appropriate isotype control, and the percentages indicate the percentages of positive cells. The results of one experiment that is representative of five experiments are shown.