FIG. 2.
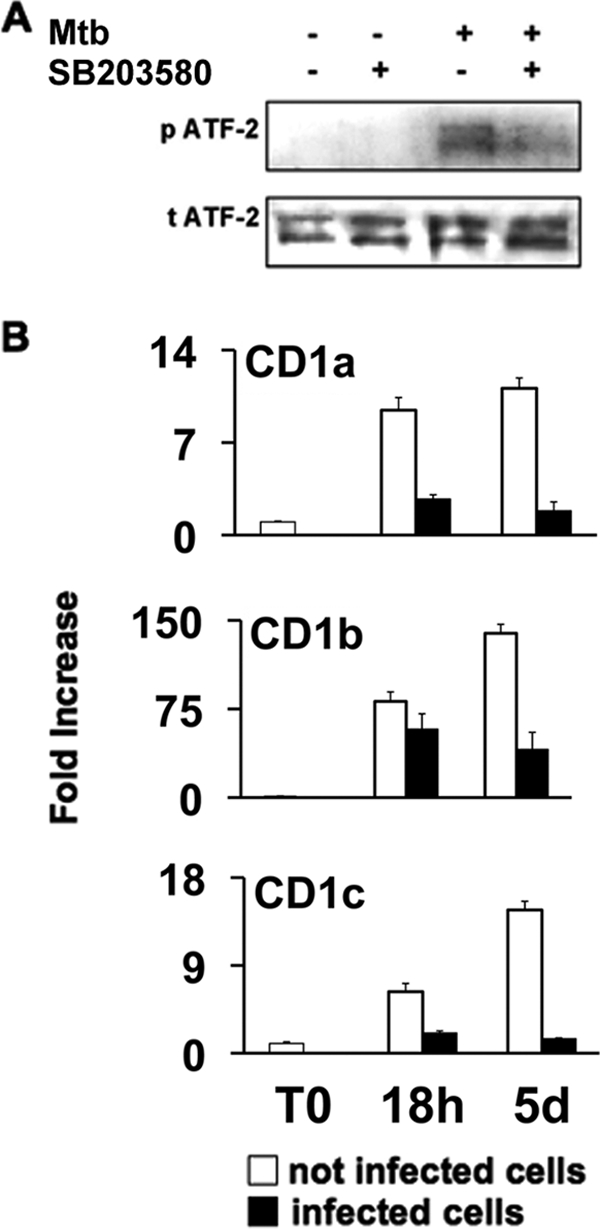
Mycobacteria activate ATF-2 through p38 phosphorylation and inhibit CD1 gene expression. (A) Monocytes were pretreated or not pretreated with p38 inhibitor (SB203580), and some of them were infected with M. tuberculosis (Mtb) for 2 h. Nuclear extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-phosphorylated ATF-2-specific antibody (p ATF-2) and anti-total ATF-2-specific antibody (t ATF-2). The results of one experiment that is representative of three experiments are shown. (B) CD1 gene expression was analyzed by quantitative reverse transcription-PCR. Untreated monocytes (open bars) and M. tuberculosis-infected monocytes (filled bars) were analyzed for CD1 mRNAs immediately after isolation (T0) and after 18 h (18h) and 5 days (5d) of culture with GM-CSF and IL-4. The mRNA levels are expressed as increases relative to the level of CD1 mRNA in freshly isolated CD1− monocytes, and the data are means and standard deviations of three replicates.
