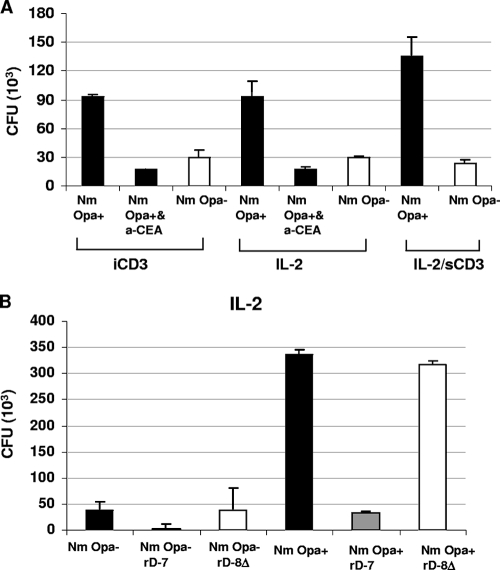
FIG. 2.
Effects of mode of CD4+ T-cell activation and blocking agents on bacterial adhesion. (A) For quantitative analysis of the binding of Opa+ or Opa− variants of N. meningitidis (Nm) to stimulated CD4+ T cells, various conditions were used. These included prestimulation of T cells with iCD3 antibody at 2 μg/ml and prestimulation with IL-2 at 200 U/ml. In both cases, after the stimulation period of 48 h, the cells were washed and infected with N. meningitidis in the absence or presence of anti-CEACAM antibody A0115 (a-CEA; 50 μg/ml). The condition labeled IL-2/sCD3 represents experiments in which IL-2-prestimulated T cells were inoculated with bacteria in the presence of anti-sCD3 antibody at 1 μg/ml. (B) CD4+ T cells were prestimulated with IL-2 for 48 h and then incubated for 1 h with recombinant polypeptide rD-7 (CEACAM-binding peptide) or rD-8Δ (control peptide) at 2 μg/ml before infection with N. meningitidis. Bacterial binding was assessed after a 3-h infection period by viable count assays. Binding of Opa− bacteria is also shown in each case for comparison.