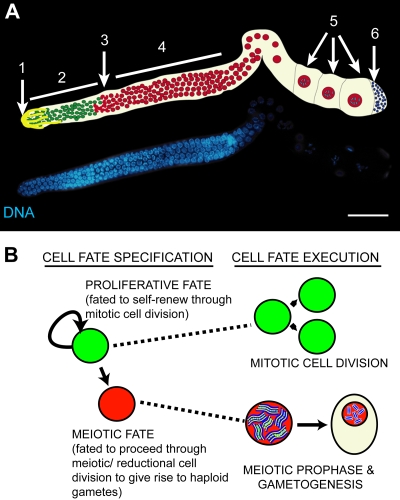
FIG. 1.
(A) Fluorescence micrograph of a dissected, DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole)-stained adult C. elegans hermaphrodite germ line, with schematic. In the distal region, proliferating germ cells (2) reside in close contact with the somatic distal tip cell (1). At the transition zone (3), germ cells enter meiosis and proceed through meiotic prophase (4) to give rise to sperm (6) and oocytes (5). (B) Scheme depicting the decision that C. elegans germ line stem cells make between maintaining a proliferative fate (green) and differentiating (red) to produce gametes.