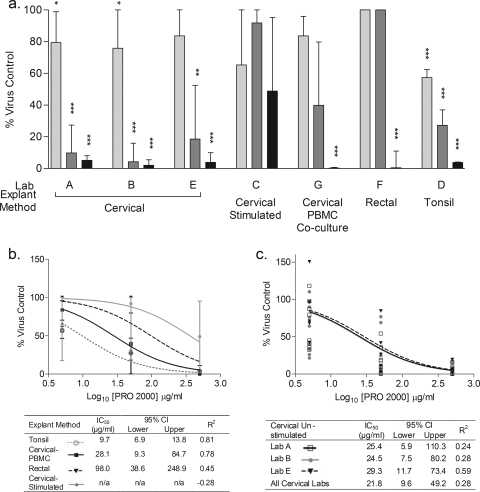
FIG. 5.
Inhibition of HIV-1Ba-L infection by PRO 2000. Inhibition of viral infection by PRO 2000 was determined for five explant tissue types (cervical, stimulated cervical, cervical tissue-PBMC coculture, tonsil, and rectal methods) in seven laboratories (A to G). (a) Median % virus control values were compared across three concentrations of PRO 2000 (5 μg/ml [ ], 50 μg/ml [
], 50 μg/ml [ ], and 500 μg/ml [
], and 500 μg/ml [ ]) to 100% virus control, where significant effects of PRO 2000 are indicated as follows: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; and ***, P < 0.001 (Wilcoxon signed-rank test). Data represent the median and interquartile range of % virus control for each tissue type. (b) The IC50 for PRO 2000 was calculated using the amount of p24 released at the assay SOFT and derived by nonlinear regression analysis for each tissue type (stimulated cervical, cervical tissue-PBMC coculture, rectal, and tonsil tissue). (c) The IC50 for PRO 2000 was calculated using the amount of p24 released at the assay SOFT and derived by nonlinear regression analysis for each laboratory using unstimulated cervical tissue (labs A, B, and E). Data represent the replicate % virus control for each lab. The embedded tables in panels b and c outline the individual IC50 (μg/ml) values, upper and lower 95% confidence intervals, and the goodness of fit (R2) of each curve. n/a, values could not be estimated with confidence from the nonlinear regression analysis.
]) to 100% virus control, where significant effects of PRO 2000 are indicated as follows: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; and ***, P < 0.001 (Wilcoxon signed-rank test). Data represent the median and interquartile range of % virus control for each tissue type. (b) The IC50 for PRO 2000 was calculated using the amount of p24 released at the assay SOFT and derived by nonlinear regression analysis for each tissue type (stimulated cervical, cervical tissue-PBMC coculture, rectal, and tonsil tissue). (c) The IC50 for PRO 2000 was calculated using the amount of p24 released at the assay SOFT and derived by nonlinear regression analysis for each laboratory using unstimulated cervical tissue (labs A, B, and E). Data represent the replicate % virus control for each lab. The embedded tables in panels b and c outline the individual IC50 (μg/ml) values, upper and lower 95% confidence intervals, and the goodness of fit (R2) of each curve. n/a, values could not be estimated with confidence from the nonlinear regression analysis.