FIG. 5.
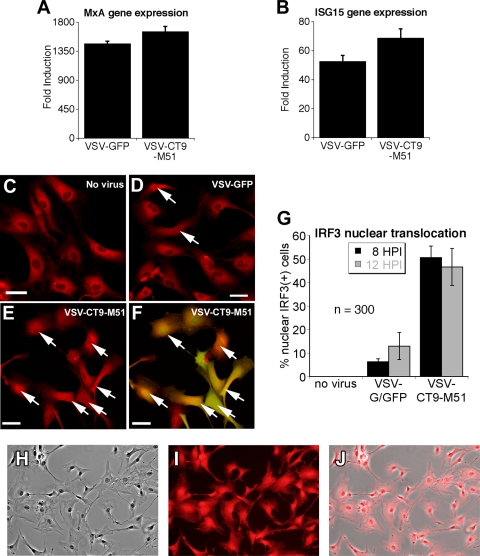
Human adult astrocytes mount a robust response to VSV-CT9-M51. (A and B) Expression of two downstream interferon genes (ISG15 and MxA) was measured with quantitative reverse transcription-PCR in primary cultures of adult human astrocytes after 6 h of incubation with VSV-G/GFP or VSV-CT9-M51. A more robust induction in interferon-induced gene expression was observed after infection with VSV-CT9-M51 than after infection with VSV-G/GFP. The error bars indicate standard errors. (C to F) Immunofluorescence for the IRF3 transcription factor was used to support the data in panels A and B. IRF3 is a key transcription factor for interferon response that is translocated to the nucleus upon interferon signaling. The arrows mark cells with nuclear labeling of IRF3, indicating nuclear translocation. Significantly more nuclear translocation of IRF3 was demonstrated in adult human astrocytes after VSV-CT9-M51 infection (E) than after VSV-G/GFP infection (D) at two time points (HPI, hours p.i.) after VSV infection (G), which is demonstrated by viral GFP expression (F). Scale bars, 35 μm. (H to J) Immunostaining of cultured cells from adult human brain tissue revealed 100% astrocytic origin. Micrographs are 225 μm wide.