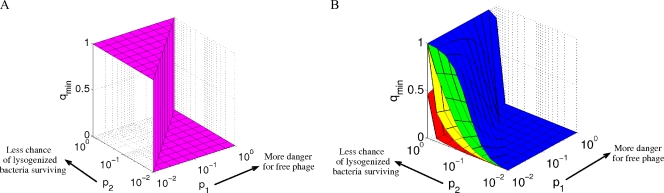
FIG. 4.
(A) Optimal strategies for the phage game for one player. The qmin strategy, which minimizes the chance of phage extinction, is deterministic: always go lytic (qmin = 1) when p1 is <p2, and always go lysogenic (qmin = 0) when p1 is >p2. All stochastic strategies result in a greater chance of extinction. (B) Optimal strategy for the phage game with n identical players. Blue, n = 2; green, n = 4; yellow, n = 10; red, n = 100. As there is a collective reward for going lytic, if the chance of free phage dying is low, the ideal situation is that in which one infected bacterium is lysed, leaving the rest to go lysogenic. This is possible only with the use of a stochastic strategy, because each player is using the same strategy. If the danger of going lytic is above a certain threshold (p1 > p2), however, then the best strategy is to deterministically go lysogenic.