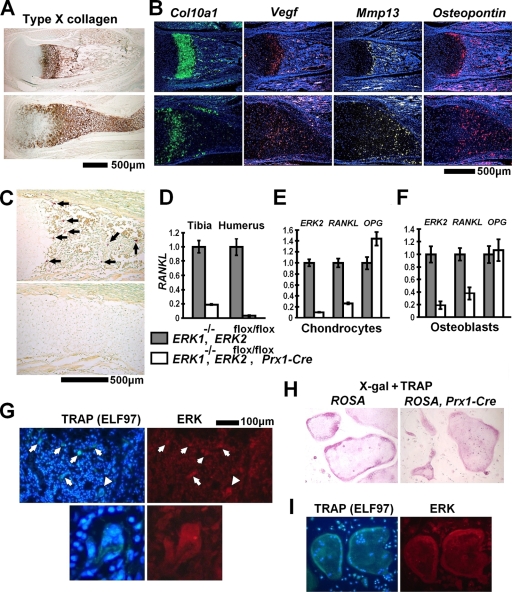
FIG. 5.
Delayed formation of primary ossification centers in ERK1−/−; ERK2flox/flox; Prx1-Cre mice. (A) Immunohistochemistry for type X collagen showed a widening of the zone of hypertrophic chondrocytes in the tibiae of ERK1−/−; ERK2flox/flox; Prx1-Cre mice at P0. (B) In situ hybridization for Col10a1, Vegf, Mmp-13, and Osteopontin showed an expansion of terminally differentiated chondrocytes in the hypertrophic zone of the tibia at P0. (C) TRAP staining showed an absence of TRAP-positive cells in the tibiae of ERK1−/−; ERK2flox/flox; Prx1-Cre embryos at E16.5. Arrows indicate TRAP-positive cells. The upper images in panels A, B, and C show ERK1−/−, and the lower images show ERK1−/−; ERK2flox/flox; Prx1-Cre mice. (D) Real-time PCR showed reduced RANKL expression in the tibiae and humeri of ERK1−/−; ERK2flox/flox; Prx1-Cre embryos at E16.5. (E, F) ERK2, RANKL, and Osteoprotegerin (OPG) expression examined by real-time PCR. Inactivation of ERK2 strongly inhibited RANKL expression in ERK1−/−; ERK2flox/flox rib chondrocytes (E) and calvarium osteoblasts (F) in vitro. RNA was extracted from ERK1−/−; ERK2flox/flox chondrocytes and osteoblasts 5 days and 8 days after infection with Ad expressing Cre recombinase or GFP. (G) ELF97-based fluorescent TRAP staining (green fluorescence) in combination with immunofluorescence for ERK protein (red fluorescence), showing the presence of ERK protein in TRAP-positive osteoclasts (arrows) in the femoral metaphysis of an ERK1−/−; ERK2flox/flox; Prx1-Cre mouse at P0. The immunofluorescent signal for ERK protein was indistinguishable from that of ERK1−/−; ERK2flox/flox mice (data not shown). The lower panels show a magnification of an osteoclast indicated by arrowheads in the upper panels. Nuclei were visualized by DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole). (H) X-Gal staining followed by TRAP staining showing no β-galactosidase activity in TRAP-positive osteoclast-like cells derived from spleen cells of Prx1-Cre mice harboring the ROSA-LacZ reporter allele (right panel). The staining results were indistinguishable from those observed for TRAP-positive osteoclast-like cells derived from control ROSA-LacZ reporter mice (left panel). (I) Spleen cells from ERK1−/−; ERK2flox/flox; Prx1-Cre mice formed TRAP-positive multinucleated osteoclast-like cells in the presence of M-CSF and RANKL (left panel). Nuclei were visualized by DAPI. These osteoclast-like cells express ERK protein (right panel), and the staining intensity was indistinguishable from that of osteoclast-like cells generated from spleen cells of ERK1−/−; ERK2flox/flox mice (data not shown).