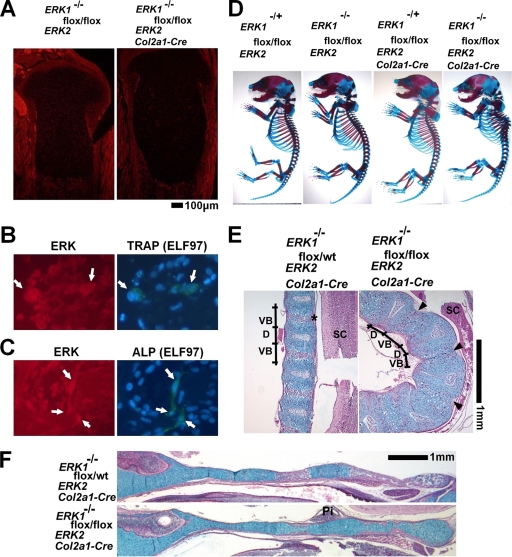
FIG. 6.
ERK1−/−; ERK2flox/flox; Col2a1-Cre embryos. (A) Immunofluorescence using anti-ERK1 and ERK2 antibody showed reduced immunoreactivity in chondrocytes in the tibiae of ERK1−/−; ERK2flox/flox; Col2a1-Cre embryos at E18.5. (B) ELF97-based fluorescent TRAP staining in combination with immunofluorescence for ERK protein, showing the presence of ERK protein in TRAP-positive osteoclasts (arrows) of ERK1−/−; ERK2flox/flox; Col2a1-Cre embryos. (C) ELF97-based fluorescent alkaline phosphatase staining in combination with immunofluorescence for ERK protein, showing the presence of ERK protein in alkaline phosphatase-positive osteoblasts (arrows) of ERK1−/−; ERK2flox/flox; Col2a1-Cre embryos. (D) Skeletal preparation after alizarin red and alcian blue staining. ERK1−/−; ERK2flox/flox; Col2a1-Cre embryos showed severe kyphotic deformity in the thoracic spine at E18.5. (E, F) Hematoxylin, eosin, and alcian blue staining of the spine (E) and cranial base (F) showing an absence of ossification centers in ERK1−/−; ERK2flox/flox; Col2a1-Cre embryos at E18.5. * indicates the ossification center in the vertebral body, and arrowheads indicate the corresponding areas in ERK1−/−; ERK2flox/flox; Col2a1-Cre embryos. VB, vertebral body; D, intervertebral disc; SC, spinal cord; Pi, pituitary gland; wt, wild type.