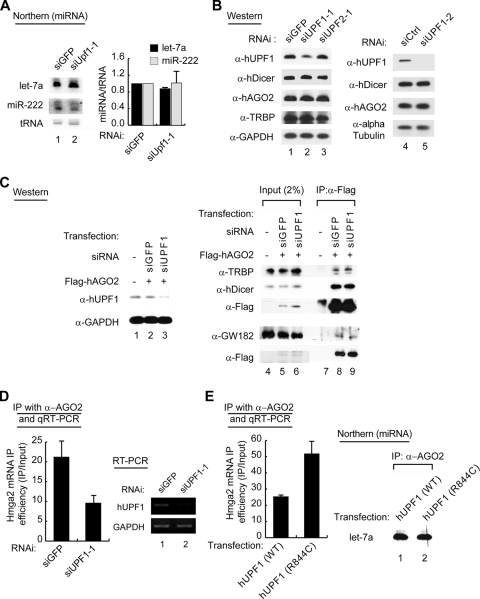
FIG. 6.
Effects of hUPF1 on hAGO2-associated mRNAs. (A) Northern blotting of miRNAs using total RNA. The graph shows the mean values (± standard deviations [SD]) of relative miRNA levels measured in two independent experiments (n = 2). (B) Western blotting of RNA silencing factors. The levels of Dicer, hAGO2, and TRBP proteins are not affected by hUPF1 knockdown. GAPDH or alpha-tubulin was used as the loading control. α, anti. (C) IP followed by Western blotting shows that the interactions between RISC components are not affected by knockdown of hUPF1. HeLa cells were cotransfected with Flag-tagged hAGO2 plasmids and siUPF1 or siGFP. IP was carried out using anti-Flag antibody in the presence of RNase A. (D) Knockdown of hUPF1 reduces the Hmga2 mRNA associated with hAGO2. hUpf1 depleted-HeLa cells were lysed and used for IP with antibody against hAGO2. Coprecipitated mRNA was extracted and quantified by qRT-PCR. The Hmga2 mRNA levels were normalized against the GAPDH mRNA levels in the same sample. The IP efficiency was then calculated by dividing the normalized Hmga2 mRNA level from IP by that for the input (n = 2; means ± SD). (E) qRT-PCR shows that overexpression of mutant hUPF1 (R844C) increases the level of hAGO2-associated Hmga2 mRNA, compared to overexpression of wild-type hUPF1 (WT). A Flag-tagged wild-type hUPF1 (WT) or mutant hUPF1 expression plasmid was transfected into HeLa cells. The cells were lysed and used for IP with antibody against hAGO2. IP efficiency was calculated as for panel D (n = 2; means ± SD). Northern blotting of miRNA (right) shows that hAGO2-associated let-7 miRNA was not affected by overexpression of mutant hUPF1 compared to overexpression of the wild type.