FIG. 5.
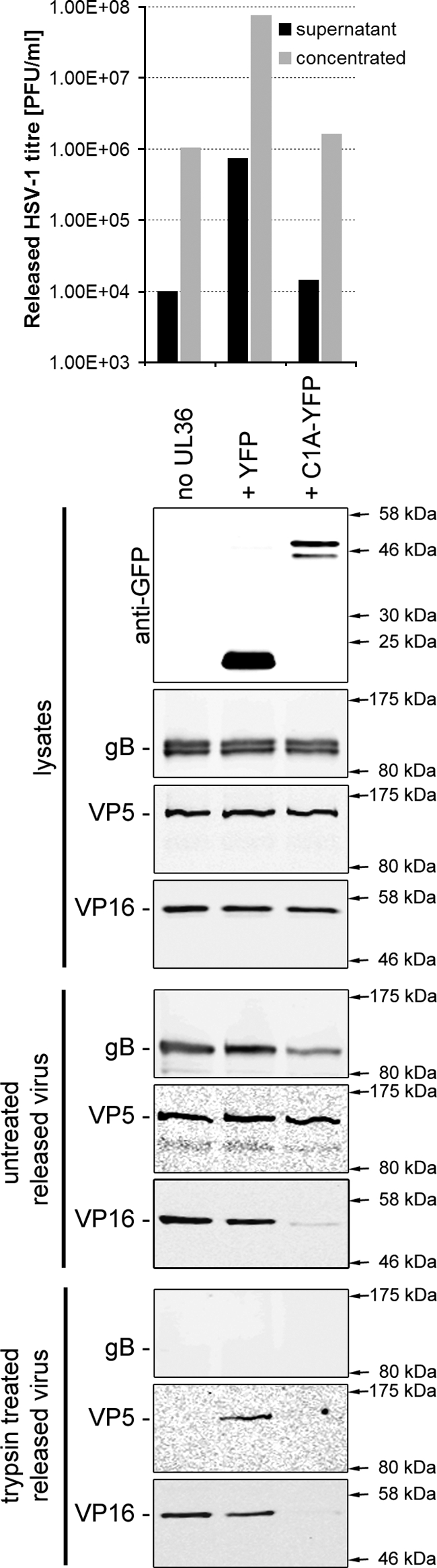
Dominant negative CHMP1A blocks the release of HSV-1 particles from infected cells. COS-7 cells were left untreated or cotransfected with a plasmid expressing UL36, together with a plasmid expressing YFP or CHMP1A-YFP. Cells were infected 24 h posttransfection with HSV-1 KΔUL36 at 5 PFU/cell. At 24 h postinfection cell culture medium samples were collected and clarified by low-speed centrifugation. Released (supernatant) HSV-1 particles were harvested by high-speed centrifugation (20,000 rpm, 4°C, 60 min; SW 40Ti rotor) and resuspended in a small volume of PBS to concentrate the released HSV-1 fraction. The infectious HSV-1 titers in the superna-tant and concentrated HSV-1 samples were determined by plaque assay on a UL36 complementing cell line (HS30; upper panel). Concentrated HSV-1 particles were treated with PBS (untreated) or 200 μg of trypsin/ml at 37°C for 1 h. The reactions were stopped by the addition of protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche). Protein samples were harvested from infected cells and samples analyzed by Western blotting for the presence of YFP-tagged proteins in cell lysates and HSV-1 envelope (gB), capsid (VP5), and tegument (VP16) proteins in all samples (lower panels).
