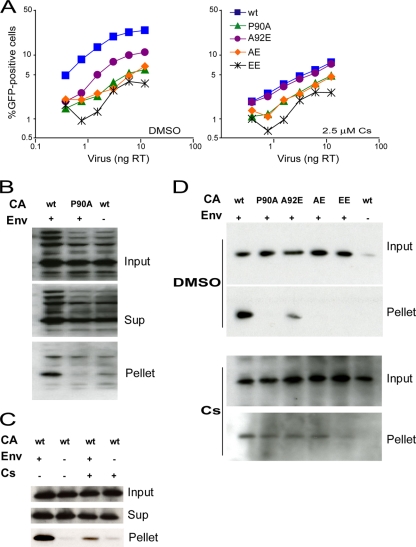
FIG. 8.
Infectivity and fate of the capsid of HIV-1 CA variants in Jurkat T lymphocytes. (A) Jurkat cells were infected in the presence of DMSO or 2.5 μM Cs with the indicated amounts of wild-type or mutant HIV-1-GFP. The results shown are typical of those obtained in three independent experiments. (B) The fate-of-capsid assay was optimized for the study of HIV-1 infection of Jurkat cells. VSV-G-pseudotyped (Env+) wild-type or P90A HIV-1 virions were concentrated, normalized by total RT activity and then incubated with Jurkat cells. As a control, virions lacking envelope glycoproteins (Env−) were studied in parallel. Four hours after infection, the cells were washed and incubated at 37°C in fresh medium for another 12 h. After lysis of the target cells, cytoplasmic lysates were analyzed directly (“Input”) or were separated over a 50% sucrose cushion into supernatant (“Sup”) and particulate (“Pellet”) fractions. The fractions were analyzed by Western blotting, with a monoclonal anti-HIV-1 p24 antibody. (C) An experiment similar to that described in panel B was carried out, except that 5 μM Cs was added to the Jurkat cell medium as indicated. (D) HIV-1 CA variants were analyzed in an experiment similar to that described in panel B in the presence of DMSO (upper panel) or 5 μM Cs (lower panel). Note that the lower panel was exposed longer than the upper panel. The results of a single experiment are shown; the experiment was repeated twice, with comparable results. wt, wild type.