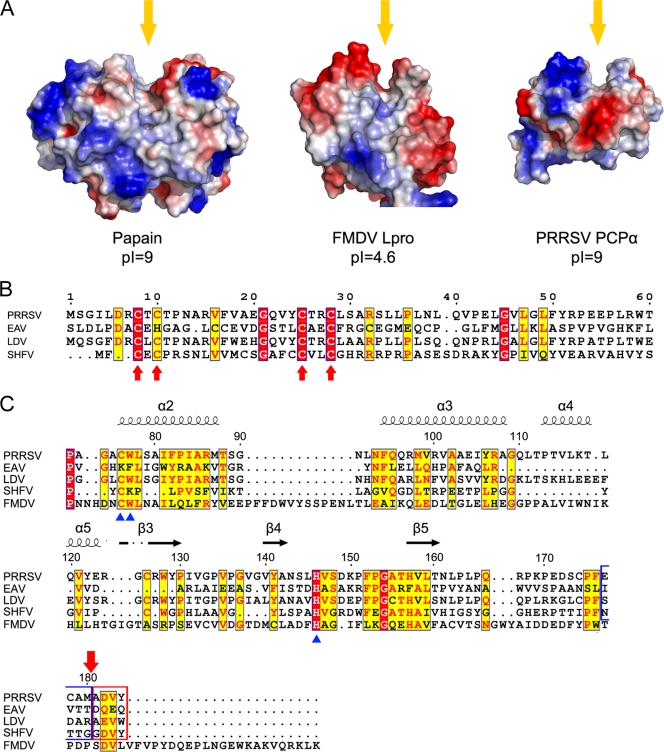
FIG. 4.
Structural and sequence comparisons of nsp1α homolog proteins. (A) Comparison of surface electrostatic potential of the PCP catalytic centers of papain (PDB accession no. 9PAP), FMDV Lpro (PDB accession no. 1QOL), and PRRSV PCPα (residues Pro66 to Gln166). Yellow arrows indicate the substrate binding grooves. (B) Sequence alignment of the N-terminal domains from PRRSV, EAV, LDV, and SHFV. Key residues of the C4 motif are marked with red arrows. Residue numbers at the top refer to the PRRSV sequence. (C) Sequence alignment of the C-terminal domains from PRRSV, EAV, LDV, SHFV, and FMDV Lpro. Key residues for the proteolytic activity of PCPs are marked with blue triangles at the bottom. Secondary-structure elements of PRRSV nsp1α are marked on top of the alignment; α-helices and β strands are presented as curves and arrows, respectively. Four residues upstream and downstream of the cleavage site of PRRSV nsp1α are highlighted with blue and red frames, and the cleavage site is marked with a red arrow on the top. The residue numbers on the top refer to the PRRSV sequence. The sequences were aligned with CLUSTALW (17), and the alignment was drawn with ESPript (7).