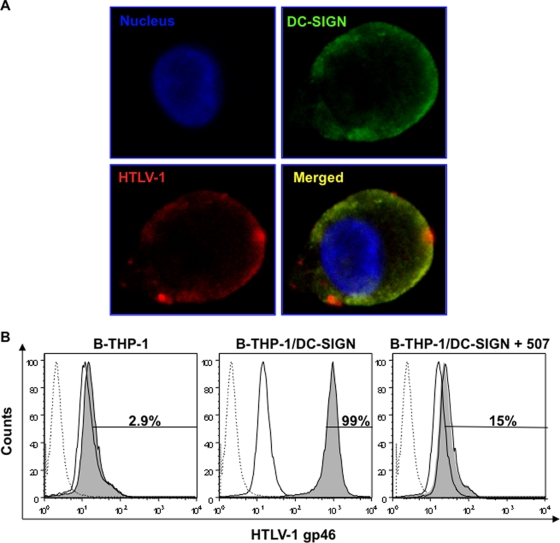
FIG. 2.
HTLV-1 colocalizes with DC-SIGN on B-THP-1 cells. (A) A fraction of cells from the QDot binding assay were analyzed by confocal microscopy. Biot-HTLV-1/Strep-QDot-bound DCs were plated on poly(D)-lysine-coated slides, fixed, and incubated with an anti-DC-SIGN MAb (1:80; clone 507) and then by an Alexa Fluor 488 (1:200)-conjugated secondary Ab. Confocal microscopy at 100× magnification demonstrated that HTLV-1 (red) colocalized specifically with DC-SIGN (green) in a uniformly but occasionally patchy configuration. Hoechst 33342 (blue) was used to demarcate the nucleus. (B) FACS analyses were performed to reconfirm the DC-SIGN-mediated binding of HTLV-1 to B-THP-1 cells. Parental and DC-SIGN-transduced B-THP-1 cells were incubated with HTLV-1 in the absence or presence of a blocking Ab against DC-SIGN (clone 507; 20 μg/ml). Unbound virus particles were removed by washing, and cells were incubated with an Alexa Fluor 647-labeled MAb against HTLV-1 gp46. A total of 50,000 collected events were gated to include the CD19+ population. The dotted-line histogram represents the isotype Ab; a solid-line histogram indicates the results obtained with untreated cells, and the filled histogram represents B-THP-1 cells positive for HTLV-1 gp46. The results shown are representative of one of the two independent experiments.