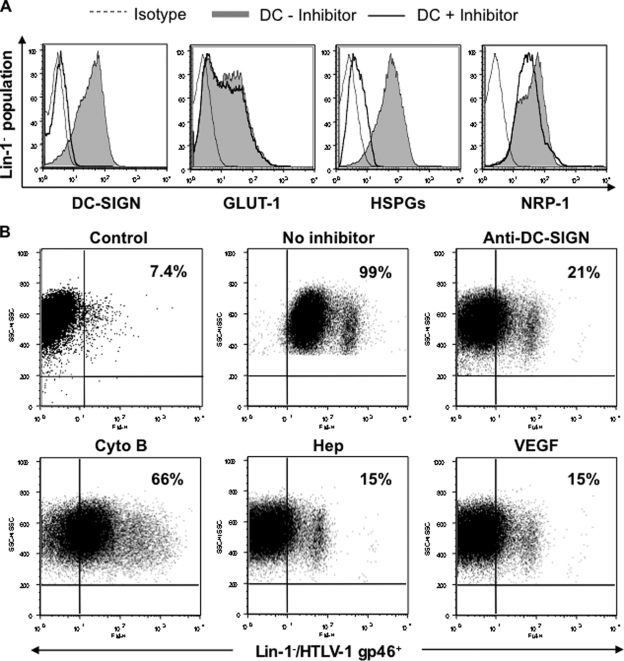
FIG. 5.
Analyses of HTLV-1 binding to MDDCs. Immature DCs were differentiated from highly purified monocytes, and their phenotype was determined using a FITC-labeled lineage cocktail (Lin-1) to determine the absence of other leukocytes. (A) To detect the presence of various HTLV-1-binding receptors on DCs, immature DCs were incubated with a FITC-labeled Lin-1 Ab in combination with APC-labeled anti-DC-SIGN, Alexa Fluor 647-labeled anti-GLUT-1, or anti-HSPGs and PE-labeled anti-NRP-1 Abs and was analyzed by flow cytometry. A total of 50,000 events collected for each sample were gated to include the Lin-1− population. Isotype controls are represented by dotted-line histograms, whereas filled histograms represent the corresponding Ab binding on untreated MDDCs. Solid-line histograms represent receptor expression postincubation (30 min) with the respective inhibitor. The results are representative of MDDCs differentiated from six different donors. (B) Immature DCs (1 × 106) either were left untreated or were treated (30 min, room temperature) with a DC-SIGN-blocking Ab (clone 507; 20 μg/ml), Cyto B (20 μM), Hep (20 mU), or VEGF (50 ng/ml). Cells subsequently were incubated with cell-free HTLV-1 (125 ng/106 cells) for 45 min on ice. Unbound virus particles were removed by excessive washing, and viral binding was examined by flow cytometry using an Alexa Fluor 647-labeled MAb with the HLTV-1 envelope glycoprotein gp46. Following appropriate color compensation, live cells collected for each sample were gated to include the Lin-1−/HTLV-1 gp46+ population. The control sample represents non-virus-pulsed DCs to exclude the nonspecific effects of the anti-gp46 Ab. The results are representative of one of four independent experiments.