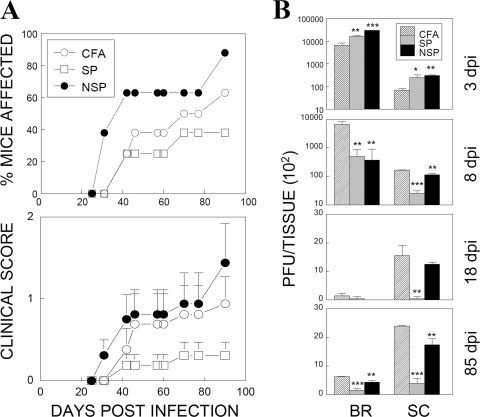
FIG. 4.
Altered TMEV-induced demyelinating disease courses in mice primed with capsid and noncapsid epitope peptides. (A) Frequency and severity of demyelinating disease development in mice preimmunized with CFA alone (n = 8), CFA plus capsid peptides (n = 8), or CFA plus noncapsid peptides (n = 8) at 7 days prior to TMEV infection. Statistical differences in disease levels between CFA and peptide-CFA groups over the course of a 42- to 90-day infection were analyzed by using a paired two-tailed t test. The incidence and severity of disease between CFA and SP-CFA groups were significantly different (P < 0.01 and P < 0.001, respectively). The differences between CFA and NSP-CFA groups were also significant (P < 0.001 and P = 0.01, respectively). To reflect the overall disease severity of each group, we included every mouse within the experimental group, regardless of disease development, in calculating disease severity scores. Error bars represent standard deviations of the group. (B) Levels of infectious virus recovered from the brains (BR) and spinal cords (SC) of experimental groups were determined by plaque assays over a course (3, 8, 18, and 85 days postinfection [dpi]) of a viral infection. Pooled CNS tissues from three to five mice per group were used due to the logistics of the plaque assays comparing different groups. The statistical significance of the differences between CFA and peptide-CFA groups were analyzed by using the Student t test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.