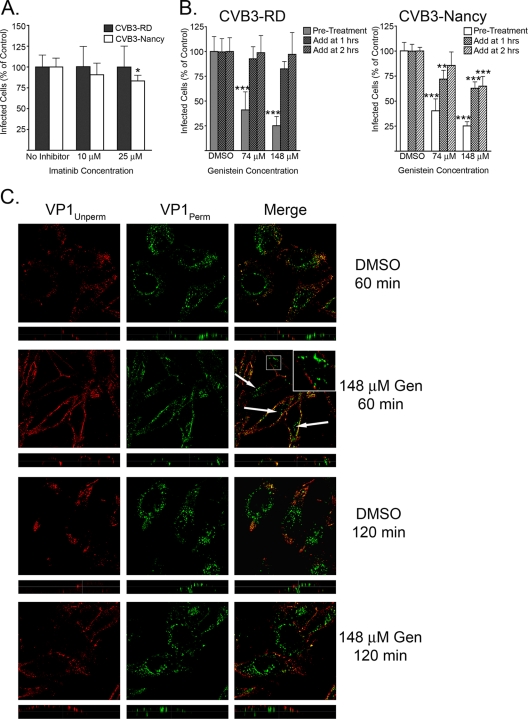
FIG. 9.
Tyrosine kinases are involved early in infection but not in internalization. (A) Imatinib-treated cells were infected with CVB3-RD or CVB3-Nancy. Cells were treated with imatinib for 1 h prior to binding, and drug was present throughout binding and infection. (B) Genistein-treated cells were infected with CVB3-RD (left graph) or CVB3-Nancy (right graph). Three conditions were tested. For condition 1, cells were treated with genistein for 1 h prior to binding, with drug present throughout binding and the first 3 h of infection (Pre-Treatment). For condition 2, genistein was added 1 h after the start of infection (Add at 1 h). For condition 3, genistein was added 2 h after the start of infection (Add at 2 h). For conditions 2 and 3, drug remained for the duration of infection. For all infection graphs, data represent the normalized percentages of cells infected ± standard deviations for duplicate samples from each of three independent experiments. (C) CVB3-RD particles were bound to and allowed to enter cells pretreated with DMSO or 148 μM genistein. Unbound virus was washed off, complete medium with genistein (Gen) was added, and virus was allowed to enter cells for 60 or 120 min. Virus was detected with a red fluorophore before permeabilization (VP1Unperm) and with a green fluorophore after permeabilization (VP1Perm). Uniquely green fluorescence indicates internalized virus. Arrows and insert identify internalized virus particles within genistein-treated cells at 60 min. Images were captured with a laser-scanning confocal microscope using an oil immersion 63× objective. Inserts within merge panels are magnified 3×. P values: *, <0.05; **, < 0.01; ***, < 0.001.