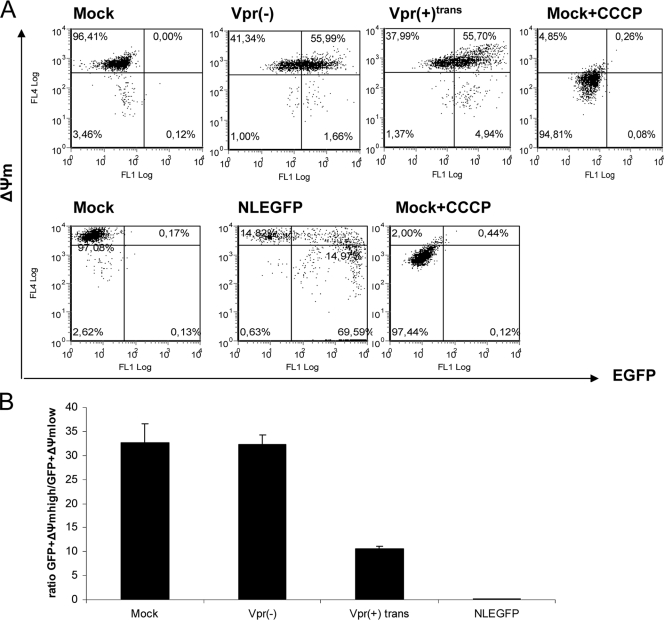
FIG. 4.
Virion-associated Vpr causes ΔΨm dissipation. (A) Jurkat cells were mock infected or infected with Vpr(+)trans or Vpr(−) viruses at an MOI of 0.5. Fifty hours postinfection, the ΔΨm was measured by using the MitoProbe DiIC1(5) assay kit. Infected cells (0.4 × 106) were labeled with 50 nM DiIC1(5) at 37°C in the dark for 30 min before analyses by flow cytometry to generate dot plots. The fluorescence intensities of EGFP and DilC1(5) are represented on the x axis and y axis, respectively. Uninfected cells treated with 250 μM of carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenyl hydrazone before being labeled with DiIC1(5) were used as a positive control. NLEGFP virus infection and subsequent staining with DiIC1(5) were used as a reference. The plots shown are representative of one of four experiments. (B) The ratio of the percentage of EGFP+ ΔΨmhigh to that of EGFP+ ΔΨmlow cells was determined for each viral infection from the dot plots and was plotted on a bar graph. The results are shown as means plus standard deviations. Note that the ratio indicated for mock infection is the ratio of the percentage of ΔΨmhigh cells to that of ΔΨmlow cells.