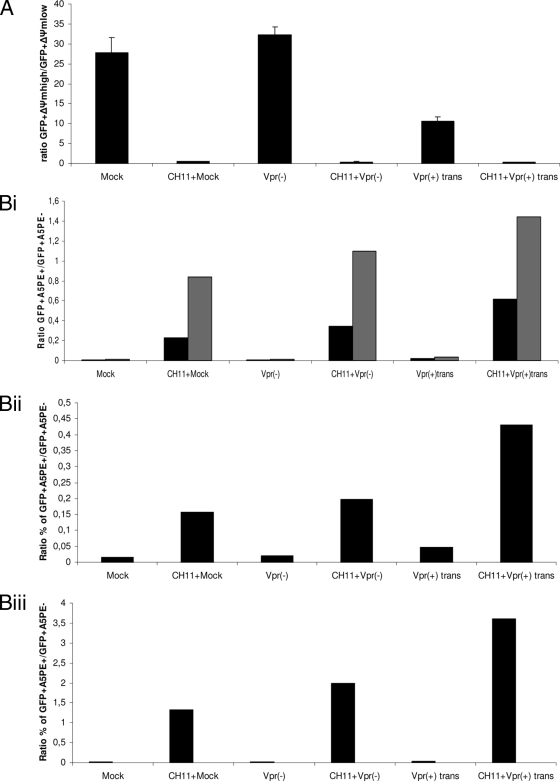
FIG. 7.
Amplification of PS exposure during Fas-induced apoptosis confirms the enhancing effect of virion-associated Vpr. Jurkat cells were mock infected or infected at an MOI of 0.5 with Vpr(−) and Vpr(+)trans viruses. Forty-six hours postinfection, the cells were treated with 12.5 ng/ml of the CH11 antibody for 4 and 8 h. Measurement of the ΔΨm was performed at 4 h post-CH11 antibody treatment, and A5PE staining was performed at 4 and 8 h post-CH11 antibody treatment (corresponding to 50 and 54 h postinfection) for each sample. The ratio of the percentage of EGFP+ ΔΨmhigh cells to that of EGFP+ ΔΨmlow cells and that of the percentage of EGFP+ A5PE+ cells to that of EGFP+ A5PE− cells were determined for each viral infection at each indicated time point from dot plots (not shown) as for Fig. 4. The calculated ratios were then plotted on bar graphs. (A) The ratios of the percentage of EGFP+ ΔΨmhigh cells to that of EGFP+ ΔΨmlow cells after 4 h of CH11 treatment are shown on a bar graph. The results are shown as means plus standard deviations. (Bi) The ratios of the percentage of EGFP+ A5PE+ cells to that of EGFP+ A5PE− cells after 4 and 8 h of CH11 treatment are shown on a bar graph. The black and gray bars represent the calculated ratios at 50 and 54 h postinfection, respectively. (Bii and Biii) Results of two other independent experiments after 4 and 8 h of CH11 treatment, respectively. Note that the ratio indicated for mock infection is the ratio of the percentage of A5PE+ cells to that of A5PE− cells and that of Δψmlow cells to that of ΔΨmhigh cells for PS exposure assessment and ΔΨm measurement, respectively.