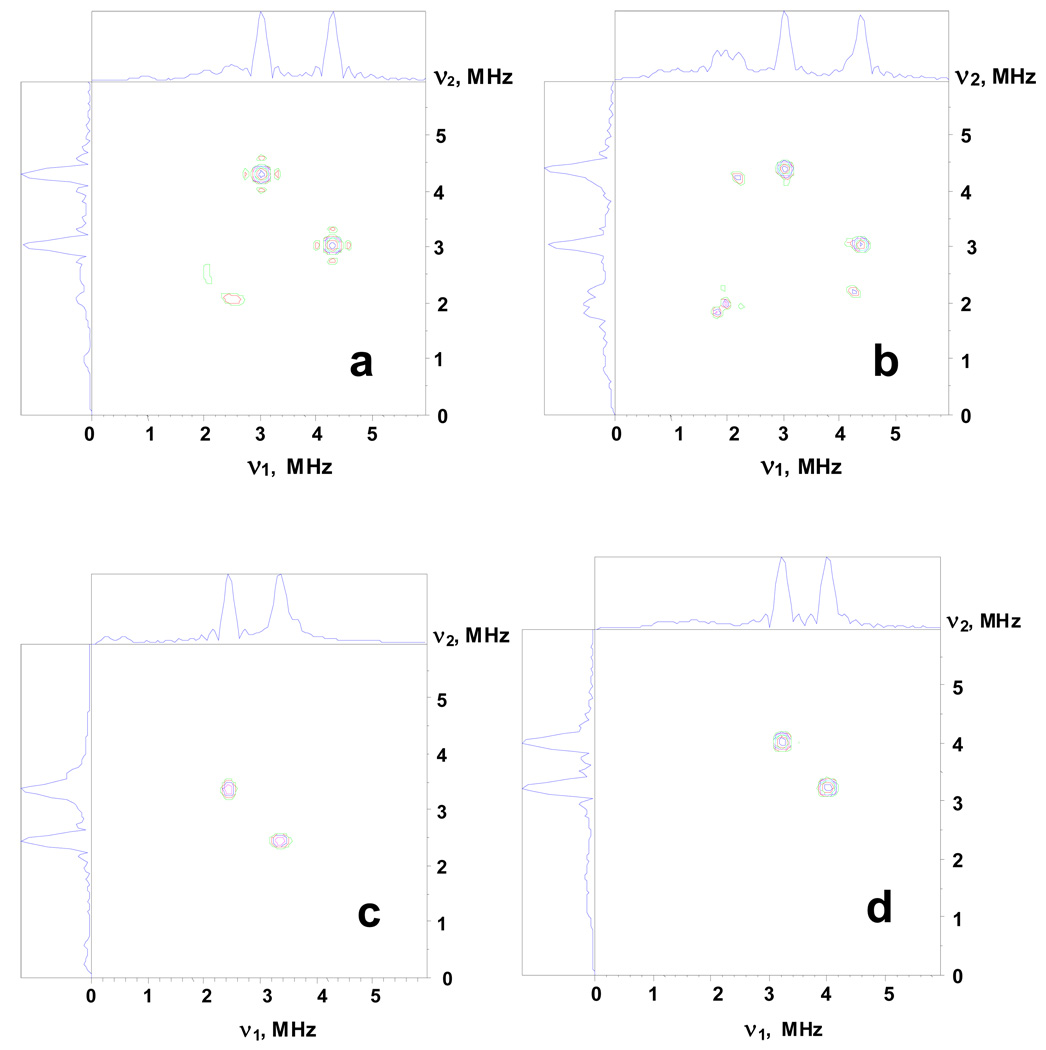
Figure 6.
14N HYSCORE spectra calculated with the following parameters: (a,b) Magnetic field Bo=343.5 mT, Bo∥g1(||) (a) and Bo=359.0 mT, Bo⊥ g1(∥) (right); relative orientation of the g-tensor and nqi tensor is described by the Euler angles (60º, 60º,0º), isotropic hyperfine constant a=1.1 MHz, quadrupole coupling constant K=0.8 MHz, asymmetry parameter η=0.5, cross-peak frequencies (4.20, 3.03) MHz (a), and (4.4, 3.03), (4.2, 2.25) MHz (b). These spectra reproduce the location of cross-peaks 1 in the spectra in Figure 4.
(c,d) Magnetic field Bo=343.5 mT, Bo∥g1(∥) (c) and Bo=359.0 mT, Bo⊥ g1(∥) (d); relative orientation of the g-tensor and nqi tensor is described by the Euler angles (0º, 90º,0º), isotropic hyperfine constant a=0.65 MHz, quadrupole coupling constant K=0.8 MHz, asymmetry parameter η=0.5, cross-peak frequencies (3.37, 2.44) MHz (c), and (4.0, 3.23) MHz (d). These spectra reproduce the location of cross-peaks 2 in the spectra inFigure 4. The time τ between first and second microwave pulses is equal to 136 ns for all spectra. The weak anisotropic hyperfine interaction up to T∼0.15 MHz does not affect the spectra calculated in the approximation of the isotropic coupling only.