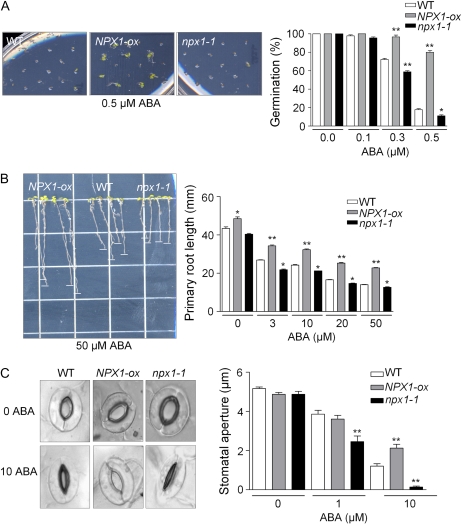
Figure 2.
Constitutive expression of NPX1 results in ABA insensitivity, while disruption of NPX1 causes ABA hypersensitivity during seed germination, inhibition of primary root growth, and stomatal closure. A, Germination of wild-type (WT), NPX1-ox, and npx1-1 seeds at 0.5 μm ABA after 5 d (left), and germination rates of seeds exposed to 0, 0.1, 0.3, and 0.5 μm ABA at 5 d (right). Data represent means ± sd of three independent experiments with 36 seeds per genotype and experiment. B, The photographs show plants of the wild type, NPX1-ox, and npx1-1 treated with 0.25× MS medium supplemented with 50 μm ABA 10 d after transfer of 6-d-old seedlings from medium without ABA (left). At right is a comparison of root elongation of wild-type, NPX1-ox, and npx1-1 seedlings; 6-d-old seedlings were transferred to plates supplemented with 0, 3, 10, 20, and 50 μm ABA, and root elongation was monitored after 6 d. Each data point represents the mean ± sd (n = 70). Asterisks indicate significant differences between the wild type and NPX1-ox or npx1-1 plants (* P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01). C, Photographs show the stomatal apertures in ABA-induced stomata closure assays with 0 (top row) and 10 μm ABA (bottom row) after 2 h of incubation. At right are stomatal aperture measurements of wild-type, NPX1-ox, and npx1-1 plants in response to 0, 1, and 10 μm ABA. Data represent means ± sd with 50 stomata per data point. Asterisks indicate significant differences between the wild type and NPX1-ox or npx1-1 plants (**P < 0.01).