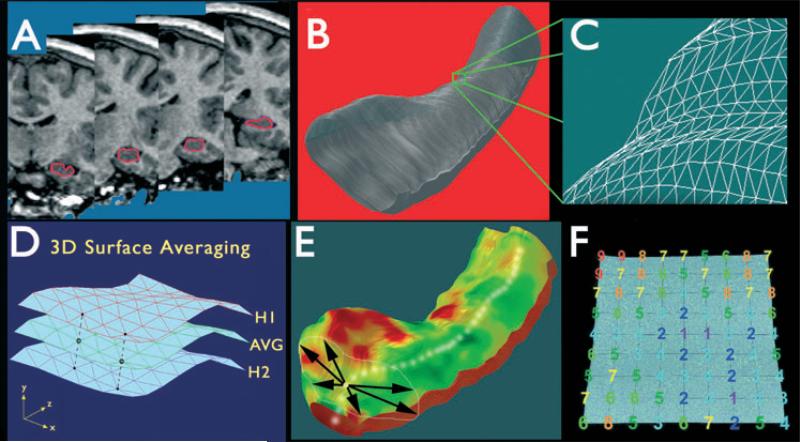
Figure 1.
Steps involved in three-dimensional (3D) hippocampal surface modeling. (A) The hippocampus is traced in contiguous coronal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) slices. (B, C) Using anatomic surface modeling software (UCLA Laboratory of NeuroImaging, LONI), traces are converted into a 3D parametric surface. (D) Surfaces from patients or controls can be averaged to produce an average anatomic model for each group. (E) On the basis of centers of mass of consecutive hippocampal traces, a medial curve is derived for each subject. (F) The distance from the medial curve to each surface point (radial size) is then calculated. Adapted from Thompson et al. (2004), with permission.