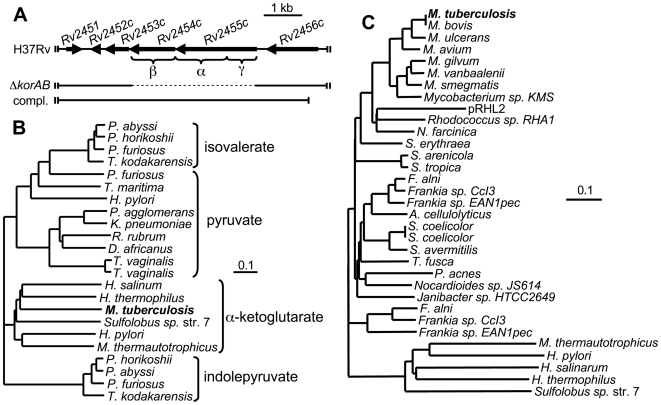
Figure 1. M. tuberculosis encodes an α-ketoglutarate: ferredoxin oxidoreductase.
(A) Genetic map of the M. tuberculosis Rv2454c-Rv2455c (korAB) region. Conserved γ, α and β domains are indicated by brackets. The bar labeled ΔkorAB denotes the region that was replaced by a hygromycin cassette using specialized transduction. The bar labeled compl. represents the region of the genome that was used for complementation of the ΔkorAB strain. (B) Phylogenetic tree of the α subunits of characterized members of the α-ketoic acid: ferredoxin oxidoreductase family. Sequences were acquired from the NCBI protein database (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov). Alignments were made by the ClustalW method, trees were reconstructed by the Neighbor Joining method using the European Bioinformatics Institute server (www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/clustalw2/index.html), graphics were generated using TreeView X (darwin.zoology.gla.ac.uk/~rpage/treeviewx/). α-ketoic acid substrates utilized by members of each clade are indicated to the right. The scale represents substitutions per residue. (C) Phylogenetic tree of α subunits of the α-ketoic acid: ferredoxin oxidoreductase found in several Actinobacteria. Alignments and trees were generated as described in B.