Figure 1.
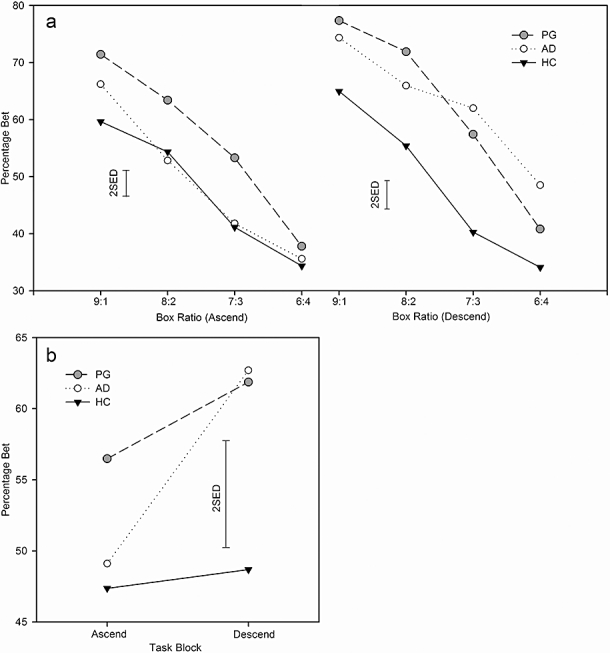
Wagering on the Cambridge Gamble Task was elevated in both alcohol-dependent (AD) and problem gambler (PG) groups, compared to healthy controls (HC). (a) Problem gamblers placed higher bets than healthy controls regardless of task condition or box ratio. (b) Betting behaviour in the ascending and descending conditions, collapsed across box ratios. Alcohol-dependent subjects placed higher bets, particularly in the descend condition. SED: standard error of the difference after Cardinal & Aitken (2006 [67]) p. 98 [SED = √(2MSerror/nh) where nh is the harmonic mean of the group sizes]
