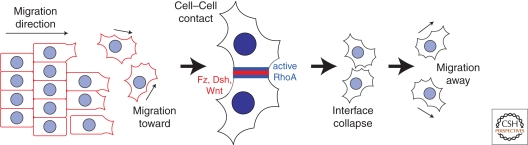
Figure 3.
PCP components regulate contact inhibition of locomotion in migrating neural crest cells. Schematic of neural crest cell migration showing cells breaking away from the epithelial sheet leading edge, migrating toward each other, and forming an interface, which then collapses and prompts cells to migrate in opposite directions. Initially, PCP components have uniform distributions, but then relocalize to the site of cell–cell contact. PCP components are required to arrest and then alter the migration path, possibly through activation of RhoA.