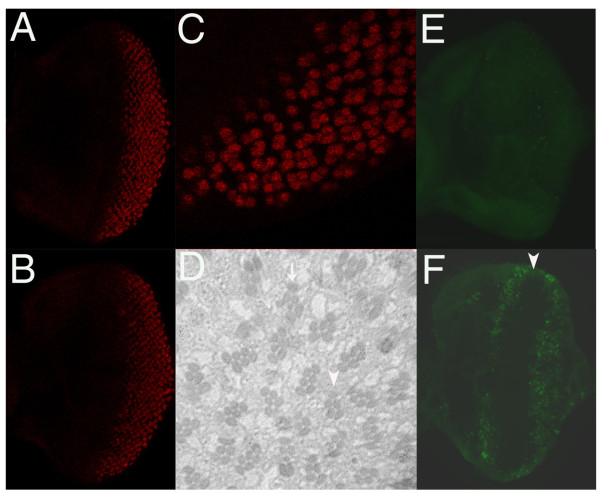
Figure 3.
rasKP mutant induces cell death in the eye. Photoreceptor differentiation, as visualized by anti-Elav staining, occurs normally in third instar larval eye discs of both wild-type (A) and rasKP mutant (B). (C) Enlarge picture of (B) showing details of pattern formation where neuronal cell recruitment and differentiation is not affected in the rasKP mutant. (D) Histological light section of an adult rasKP mutant eye showing a disarrayed pattern of ommatidia. Although the full complement of photoreceptor cell types can be found (arrow), many ommatidia occasionally contain fewer photoreceptor cells (arrow head). Acridine orange staining shows very few apoptotic cells in a wild-type eye disc (E), whereas in the rasKP mutant (F) there is a massive number of dying cells occurring as a band just anterior to the morphogenetic furrow (arrow head) and broadly in the posterior region of the eye disc. Genotypes: (A) (E) wild-type; (B) (C) (D) (F) rasKP/rasKP.