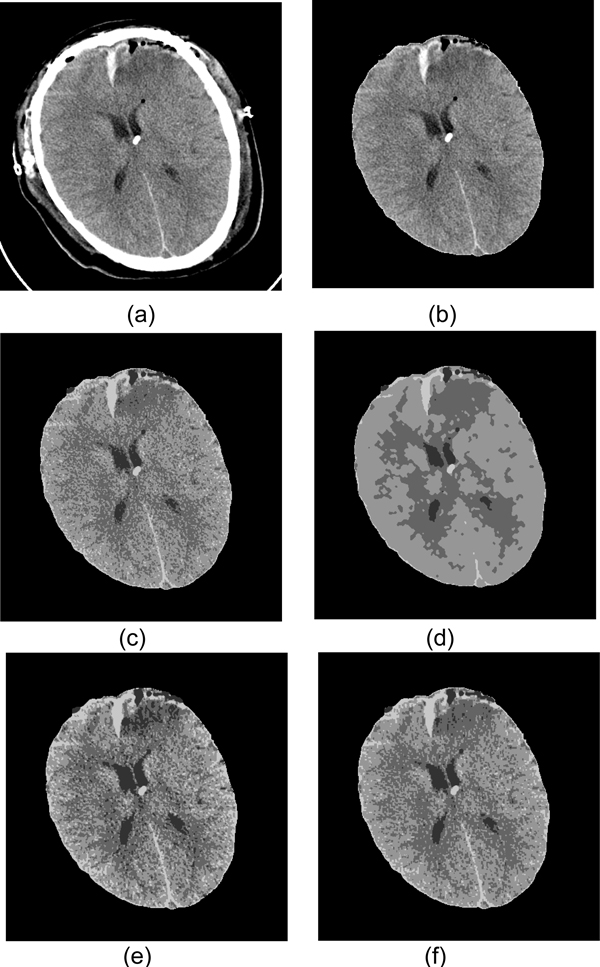
Figure 18.
Comparison of Segmentation methods. (a) Original CT Image. (b) CT Image without skull. (c) K-means clustering result. Intensity value for each pixel is used as the feature. Four clusters are specified with initial seeds. The problem for K-means is that there are holes in the result segmentation because of uneven intensity distribution for the same part as well as noise. (d) ICM segmentation result with K-means segmentation as initial result. It result smoother result, although it lose some small parts, like the tip of left horn. (e) MASP segmentation result. This result has more noise than ICM. For example, the some parts of bruise area on the right upper corner are labeled as ventricle part. (f) Modified MASP segmentation result. This result is in the middle between ICM and MASP. It has less noise than MASP but not as smooth as ICM, which supports our mathematical analysis.