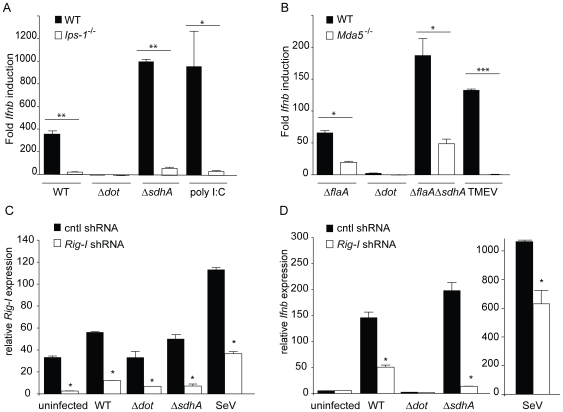
Figure 3. Hyperinduction of type I IFN by sdhA mutants involves cytosolic RNA sensing pathway components Ips-1, Rig-i, and Mda5.
(A) Hyperinduction of Ifnb by ΔsdhA L. pneumophila is largely dependent on Ips-1. Bone marrow derived Ips-1+/+ and Ips-1 −/− macrophages were infected with wild type, Δdot, and ΔsdhA L. pneumophila at an MOI of 1. Ips-1+/+ and Ips-1 −/− macrophages were transfected with 1.0 µg/ml poly I:C. 4 hours post infection and stimulation, macrophages were harvested and assessed for Ifnb induction as in Figure 1. Ips-1+/+ infected with WT L. pneumophila induced statistically significant higher levels of Ifnb transcript than Ips-1 −/− (**, p<0.005, Student's t-test). The same phenotype was seen in Ips-1+/+ infected with ΔsdhA L. pneumophila (**, p<0.005) and transfected with poly I:C (*, p<0.05) when compared to Ips-1 −/−. (B) Hyperinduction of Ifnb by ΔsdhA L. pneumophila is partially dependent on Mda5. Bone marrow derived Mda5+/+ and Mda5 −/− macrophages were infected with ΔflaA, Δdot, and ΔflaAΔsdhA L. pneumophila at an MOI of 1. Theiler's virus (TMEV) was overlaid onto Mda5+/+ and Mda5 −/− macrophages. 4 hours post bacterial and viral infection, macrophages were harvested and assessed for Ifnb induction by qRT-PCR as in Figure 1. Ifnb message was induced statistically significantly in Mda5+/+ macrophages infected with ΔflaA L. pneumophila versus Mda5 −/− (*, p<0.05, Student's t-test). Mda5+/+ also responded statistically significantly to ΔflaAΔsdhA L. pneumophila over Mda5 −/− (*, p<0.05, Student's t-test), while Theiler's virus elicited a robust Ifnb response from Mda5+/+ not seen in Mda5 −/− (***, p<0.005, Student's t-test). (C) Retroviral transduction of a Rig-i shRNA, but not the control shRNA, knocks down expression of Rig-i. MyD88 −/− Trif −/− immortalized macrophages were stably transduced with retroviral vector containing a control and Rig-i shRNA. Level of Rig-i knockdown was determined by quantitative RT-PCR under uninfected and infected conditions. Differences in Rig-i transcript levels were statistically significant (*, p<0.05, Students t-test) under resting and infected conditions. (D) Rig-i is involved in the hyperinduction of type I interferon by ΔsdhA L. pneumophila. Rig-i knockdown leads to reduced Ifnb expression in response to infection with WT and ΔsdhA L. pneumophila, as well as Sendai virus. Quantitative RT-PCR was carried out 4 hours post infection. Control knockdown macrophages induced a statistically significant (*, p<0.05) higher level of Ifnb transcript in response to WT and ΔsdhA L. pneumophila and Sendai virus. No significant difference was found in uninfected or Δdot L. pneumophila infected macrophages.