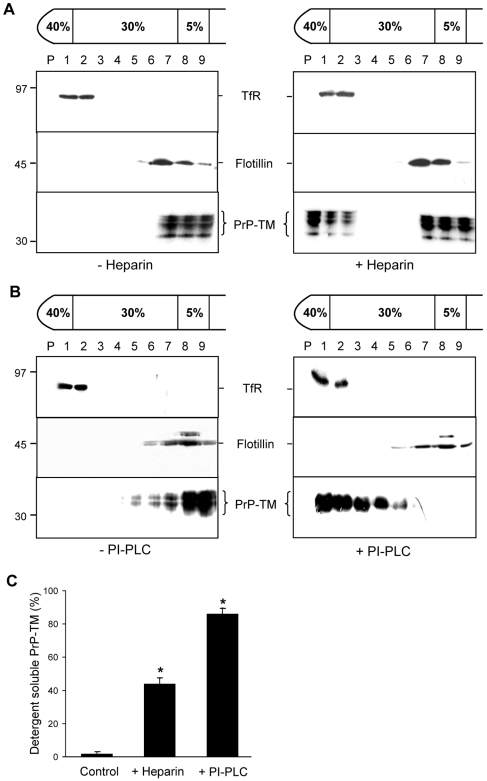
Figure 2. The association of PrP-TM with DRMs is disrupted by treatment of cells with either heparin or bacterial PI-PLC.
SH-SY5Y cells expressing PrP-TM were surface biotinylated and then (A) incubated in the absence or presence of 50 µM heparin prepared in OptiMEM for 1 h at 37°C or (B) incubated in the absence or presence of 1 U/ml bacterial PI-PLC for 1 h at 4°C. Cells were homogenised in the presence of 1% (v/v) Triton X-100 and subjected to buoyant sucrose density gradient centrifugation. PrP-TM was immunoprecipitated from equal volumes of each gradient fraction using 3F4 and subjected to western blotting. The biotin-labelled PrP-TM fraction was detected with peroxidase-conjugated streptavidin. Flotillin-1 and transferrin receptor (TfR) were detected by immunoblotting as markers for DRM and detergent-soluble fractions respectively. (C) Densitometric analysis of the proportion of total PrP-TM present in the detergent soluble fractions of the plasma membrane after heparin and PI-PLC treatment. Experiments were performed in triplicate and repeated on three occasions. * P<0.05.