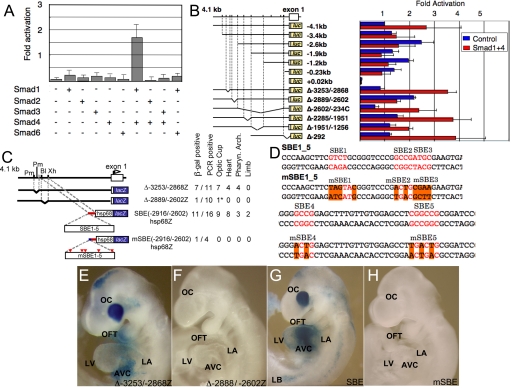
Fig. 2.
Delineation of the distal Smad factor dependent Tbx2 enhancer. (A) Multiple Smad expression vectors tranfected into CV1 cells revealed activation caused by Smad1/4 of the 4.1 kb of 5′ flanking sequence of Tbx2 fused in-frame to the luciferase. The bars represent the average of three independent transfections, and the error bars represent the SE of corrected luciferase activity relative to the pCMV5 control vector. (B) Activation by Smad1/4 required the −2889/−2602 region. (C) Schematic representation of Tbx2 transgenes analyzed in E9.5 F0 embryos and a summary of the tissue restricted expression activity. (D) Five SMAD sites in SBE1-5 were mutated by site directed mutagenesis in mSBE1-5. (E–J) LacZ expression patterns in E9.5 F0 embryos. (E) Δ−3253/−28682hsp68Z transgene; a gap deletion mutant, of a region immediately upstream of the multiSmad sites. (F) Δ−2899/−2602hsp68lacZ; a gap deletion mutant in which the multiple Smad sites were removed from the 5′ flanking sequence. (G) SBE(−2916/−2602)hsp68lacZ; the region from −2916 to −2602bp, containing five Smad sites, was linked to the hsp68lacZ reporter gene. (H) mSBE(−2916/−2602)hsp68lacZ; mutations were inserted at the multiple Smad sites in the −2916/−2602 fragment. LacZ expression were recapitulated by the DNA fragments containing Smad binding sites (E and G), whereas gap deletion and point mutagenesis of Smad binding sites eliminated gene activity in transgenic mice (F and H). Restriction sites are: BlpI; Xh, XhoI.