Fig. 2.
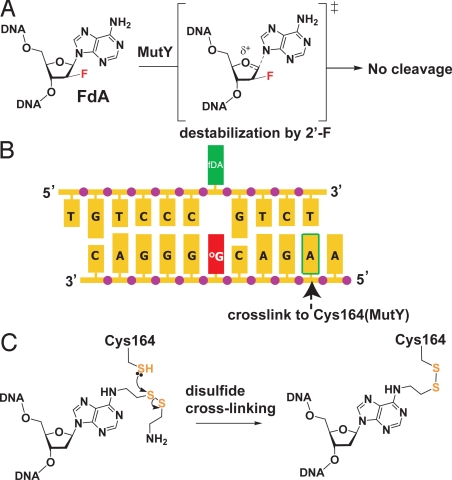
Strategy for crystallization of the fluorinated lesion-recognition complex (FLRC). (A) Introduction of a fluorine atom into the substrate dA residue destabilizes the transition state (bracketed) leading to the oxocarbenium ion intermediate in glycolytic cleavage by MutY, thereby preventing the cleavage from occurring. (B) Sequence of the duplex DNA used in this work. For experiments that used intermolecular disulfide cross-linking (DXLing), the adenine residue indicated by the arrow was modified as shown in panel C, and this was cross-linked to a mutant form of Bst MutY containing a Cys residue engineered at position-164. (C) Structure of the modified adenine used in DXLing, and of the covalent linkage it forms with Cys-164 MutY.