Fig. 1.
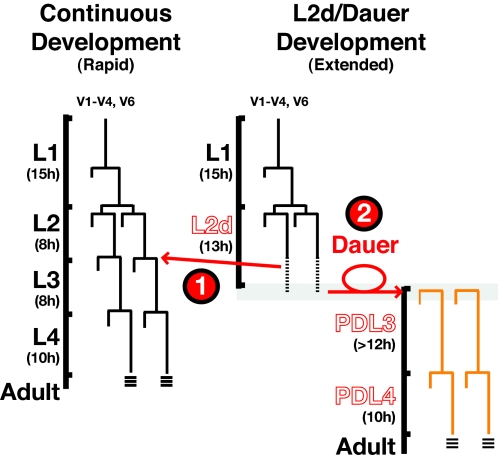
Temporal development can be modulated by environmental conditions. Wild-type seam cell lineage diagrams for both continuous (Left) and dauer (Right) life histories. In harsh environments, wild-type animals extend the chronological interval between the L1 and L2 molts (L2d). During the L2d, animals enter a critical period in which one of two life histories must be chosen to (1) resume continuous development or (2) arrest as a dauer larva. Once committed to dauer program, wild-type animals can remain in this stress-resistant form for hours to months (2). When food supplies return to favorable conditions, dauer animals will continue development to a reproductively competent adult.