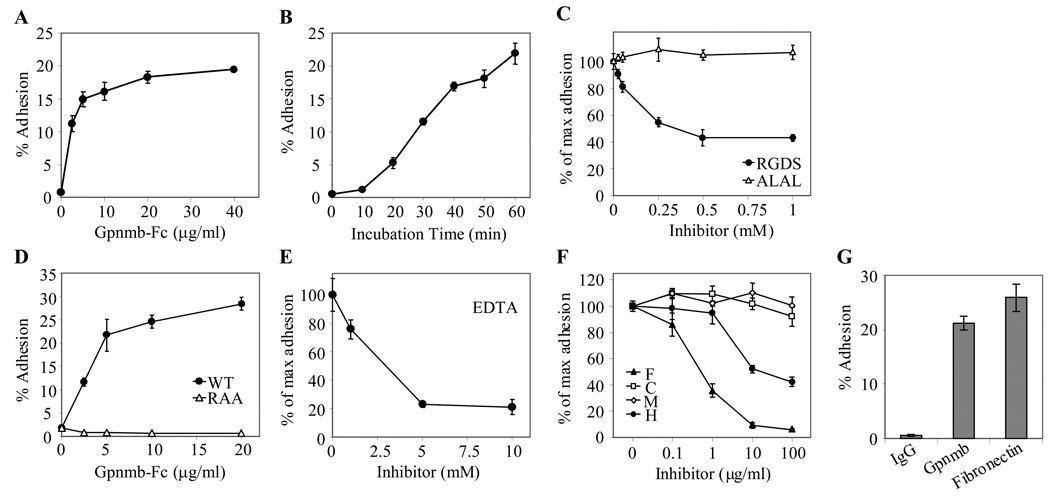
Figure 7. PAM212 keratinocytes adhere to immobilized Gpnmb in a RGD-dependent manner.
(A) Dose-dependent adhesion: 3H-thymdine-labeled PAM212 cells were allowed to adhere immobilized Gpnmb-Fc at varying doses. Adherent cells were lysed and measured for 3H-cpm. Adhesive activity is expressed as percent 3H-cpm relative to total input cpm. (B) Incubation time: At different time points after incubation of PAM212 cells with immobilized Gpnmb-Fc (20 µg/ml), adhesion to Gpnmb was assayed by 3H-cpm. (C) RGD-dependency: Adhesion of PAM212 cells to Gpnmb was blocked by addition of RGDS or ALAL (tetramer peptide) at varying doses. Adhesive activity is shown as % of maximum adhesion (without inhibitors). (D) RGD-deficient Gpnmb: PAM212 cells were incubated in 96-ELISA wells precoated with wild-type Gpnmb-Fc or RAA mutant (20 µg/ml) for 1 h. Adhesion is expressed by % adhesion of input PAM212 cells. (E and F) Effect of inhibitors on adhesion: Adhesion assay was performed in the presence of EDTA (E) or polysaccharides (F) (F, fucoidan; C, chondroitin sulfate; M, mannan; and H, heparin) at different concentrations. (G) Comparison with adhesion to fibronectin: 3H–labeled PAM212 cells were incubated for 60 min in ELISA wells precoated with IgG, Gpnmb-Fc (each 40 µg/ml) or fironectin (80 µg/ml) and adhesion measured. All data are representative of at least three independent experiments.