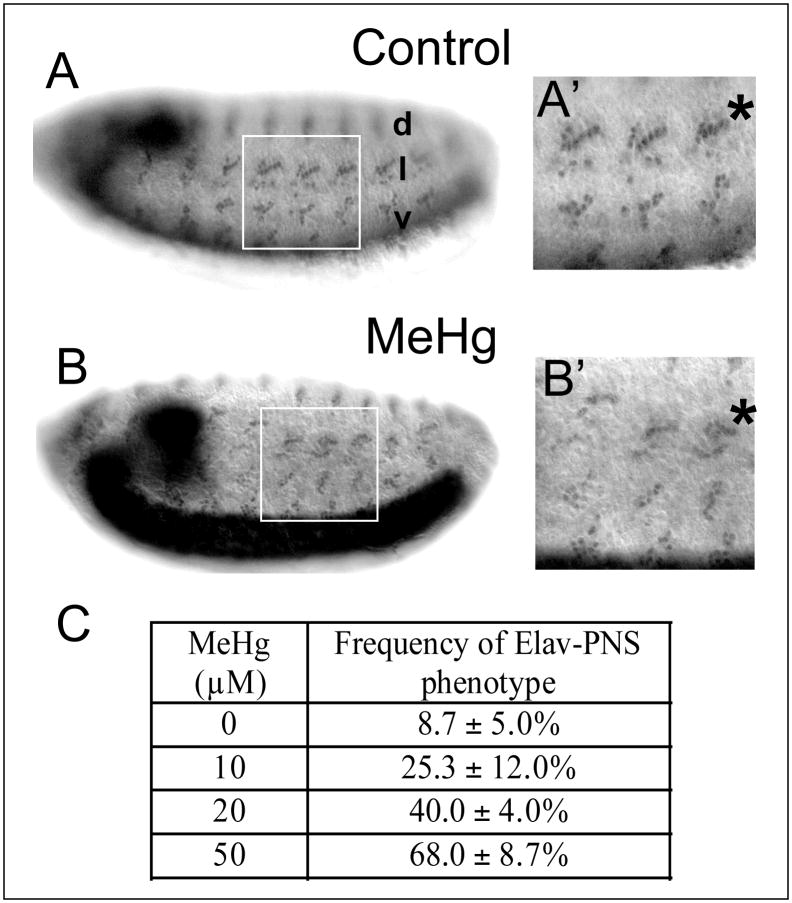
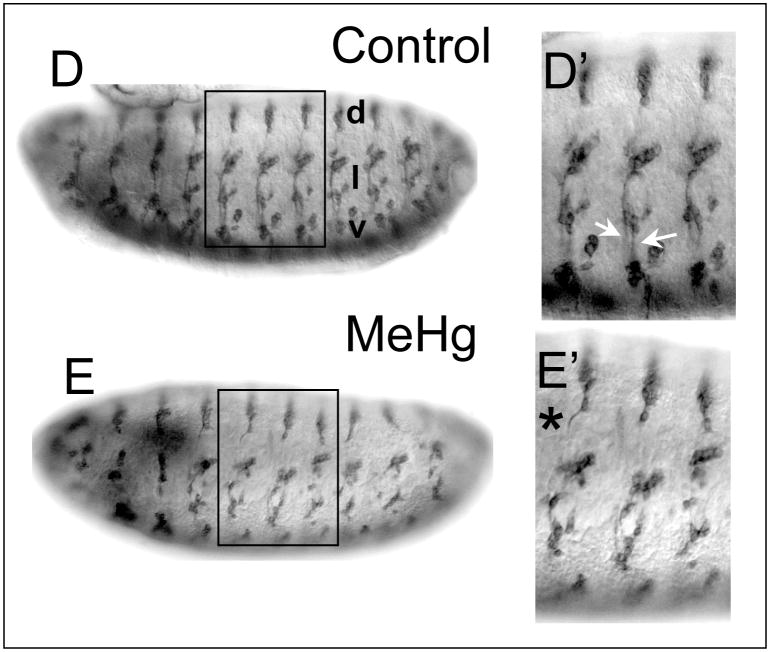
Figure 6. Defects in neural patterning and axon outgrowth in the PNS of MeHg treated embryos.
Patterning of stage 14–15 embryos PNS neurons with control (A) and MeHg (50μM) exposure (B) is revealed with the anti-elav antibody. The dorsal (d), lateral (l) and ventral (v) clusters of the PNS sensory neurons form in a stereotypical pattern in each abdominal segment (A, A′) that is disrupted with MeHg exposure (B, B′). The lateral lch5 neuron cluster is denoted by (*). (Note, the intensity difference of the VNC staining arises from the slightly different orientation of the embryos in A versus B) The frequency of the MeHg-induced PNS phenotype at various MeHg concentrations is seen in the table (C) (see methods). Average and standard deviation of three independent MeHg treatments for each concentration are shown with n=150 embryos for each data point. Axon projections of stage 14–15 embryo PNS neurons with control (D) and MeHg (50μM) treatment (E) are revealed by staining with the 22C10/Futstch antibody. Normal projections of the segmental and intersegmental nerves (white arrows, D′) in control embryos and the abnormal projection of the dorsal nerve (* E′) with MeHg are shown. (Anterior is to the left and dorsal is up. See text for discussion).