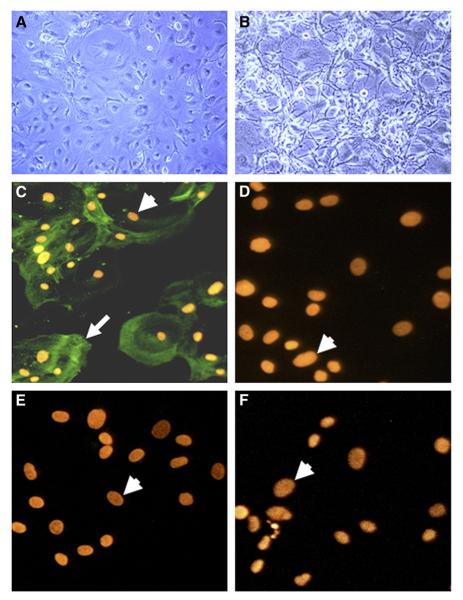
Fig. 1.
Representative photomicrographs showing human postmortem brain-derived HCSMC. Phase contrast photomicrographs showing morphology of unstimulated HCSMC (A) and IL-1β stimulated HCSMC (B) (magnification 150×). Immunofluorescence micrographs of HCSMC stained with antibodies to smooth muscle α-actin (C—magnification 650×), and CD31 (D), GFAP (E) and LN3 (F) (magnification of D, E and F—800×), and detected by reaction with Alexa 488-labeled goat-anti-mouse or -anti-rabbit secondary antibodies. Positive immunoreactivity (arrow) was only observed in cells stained with SMA antibody (C); panels D, E and F showed no reactivity. Immunoreacted cells were counterstained with propidium iodide to identify nuclei (arrowheads).