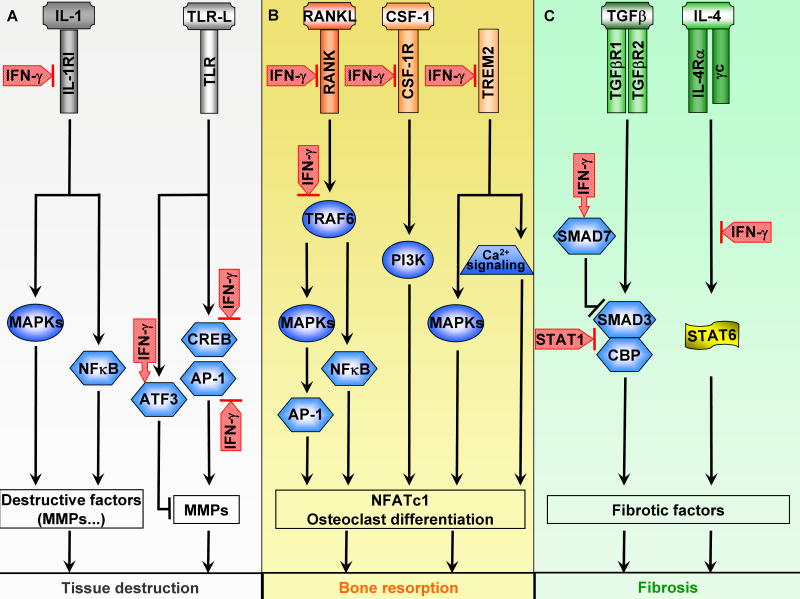
Figure 3. Signaling Mechanisms Associated with IFN-γ-mediated Attenuation of Tissue Destruction.
(A) IFN-γ suppresses inflammatory tissue destruction via regulation of IL-1R and TLR signaling. IFN-γ inhibits IL-1 signaling and subsequent induction of destructive factors in macrophages by downregulating IL-1RI expression. In addition, IFN-γ blocks induction of MMP downstream of TLR signaling by superinducing transcription repressor ATF3 and inhibiting transcription activators CREB and AP-1. IFN-γ inhibits CREB activity by suppressing its serine phosphorylation and inhibits AP-1 by downregulating nuclear protein levels of its subunits.
(B) IFN-γ inhibits osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption via regulation of RANK, CSF-1R, and TREM2 signaling. In osteoclast progenitor cells, IFN-γ suppresses expression as well as signal transduction of RANK, CSF-1R, and TREM2, receptors critical for the process of osteoclastogenesis.
(C) IFN-γ attenuates fibrosis via inhibition of TGFβR and IL-4R signaling. IFN-γ suppresses TGFβR signaling by induction of inhibitory SMAD (SMAD7) and by direct inhibition of SMAD3 by STAT1. IFN-γ inhibits IL-4R signaling by induction of SOCS1 (see Figure 5A for details).