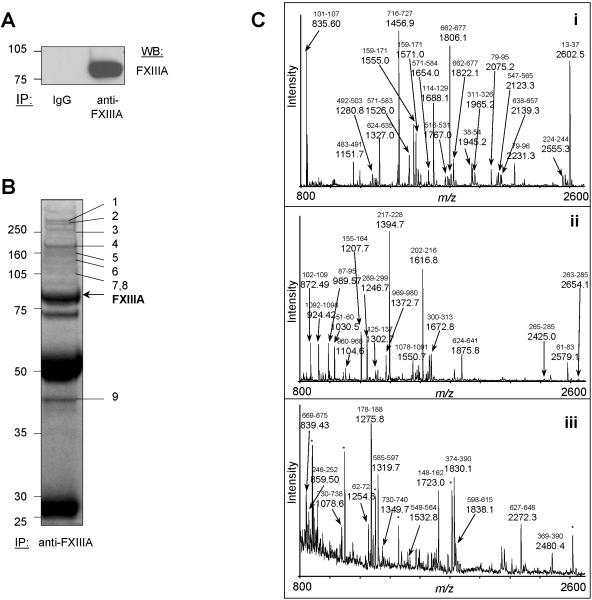
Figure 3. Immunoprecipitation and 1D-gel separation of FXIIIa-associated proteins followed by tryptic digestion, MALDI-TOF characterization and PMF assignment of immunoprecipitated proteins.
(A) A specific signal was obtained for FXIIIa after immunoprecipitation from resting platelet lysates and immunoblotting (lane “anti-FXIIIa”) compared to the non-specific isotypic control (lane “IgG”). (B) FXIIIa was immunoprecipitated from resting platelet lysate at an antibody:protein ratio of 1:80. The immunoprecipitate was separated by 1D-GE and stained with Coomassie Blue. Shown are all proteins precipitated with the anti-FXIIIa sheep antibody. All distinguishable gel bands were excised, then subjected to tryptic in-gel digestion, and analyzed by MALDI-TOF MS and PMF. FXIIIa was identified as marked. All other proteins were assigned as indicated: 1-myosin, 2-talin, 3-filamin, 4-thrombospondin, 5-vinculin, 6-integrin αIIb, 7-α-actinin, 8-FAK, and 9-actin γ (for details, see Table 1). Experiments in (A) and (B) were repeated three times. IB indicates immunoblot. (C) MALDI-TOF mass spectra were obtained after tryptic in-gel digestion of excised protein bands/spots and were analyzed by PMF. (i) FXIIIa, (ii) thrombospondin, and (iii) gelsolin. Peaks of major peptide ions, which are derived from the identified protein, are labeled with their m/z values. The corresponding amino acid interval of the assigned peptide is indicated above the m/z value (small font). Abundant but unassignable ions are labeled with <*> symbols.