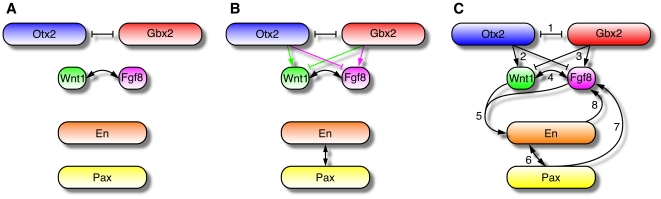
Figure 2. Regulatory networks between the IsO genes.
(A) Necessary interactions. Any valid network includes a mutual inhibition of Otx2 and Gbx2 as well as a mutual activation of Fgf8 and Wnt1. (B) Four minimal networks maintain the steady state expression pattern of the IsO genes. They are obtained by including either of the two green and either of the two magenta interactions. (C) Regulatory network obtained from literature data. It includes the following interactions: (1) The mutual repression of Otx2 and Gbx2 [5],[6]. (2) The positive regulation of Wnt1 and the negative regulation of Fgf8 by Otx2 [3],[5],[93]. (3) The positive regulation of Fgf8 and the negative regulation of Wnt1 by Gbx2 [4],[6],[25]. (4) The maintenance of Fgf8 by Wnt1 [10] and, vice versa, the maintenance of Wnt1 by Fgf8 as demonstrated herein and by [11]. (5) The synergy between Fgf8 and Wnt1 in the maintenance of En [15],[23],[26],[27]. (6) The mutual activation of En and Pax [25],[31],[32]. (7) The induction of Fgf8 by Pax [19],[94]. (8) The positive regulation of Fgf8 by En [16].