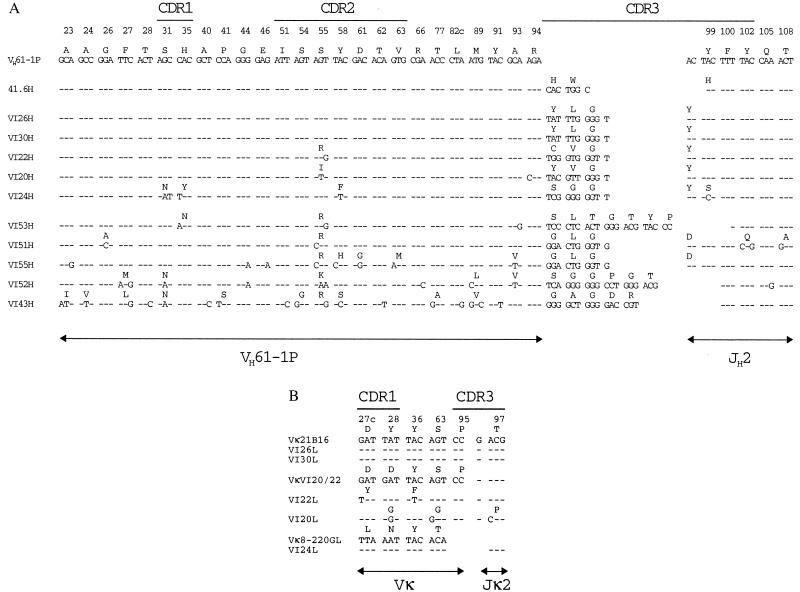
Figure 1.
Comparison of VH and VL sequences of VH7183/JH2-positive VSV-neutralizing antibodies. VH and some VL sequences of hybridomas are shown isolated from BALB/c mice 4 days after infection (41.6), isolated 12 days after primary infection and a booster infection on day 9 (VI26, VI30, VI22, VI20, and VI24), and isolated on day 150 after repeated booster infections every 3 weeks (VI53, VI51, VI55, VI52, and VI43). CDR, complementarity-determining region. (A) VH sequences are aligned with germ-line sequences of the VH61–1P gene (20) and the JH2 segment (39). Only codons differing from the germ-line sequence are shown. VH nucleotide sequence identity with reference sequences is indicated by - - -. Differences are marked by the respective nucleotide, and a change in the deduced amino acid is shown by the single-letter code. Codons are numbered according to ref. 22. (B) VL sequences are aligned with the germ-line sequences of the Vκ21B16 gene (23), the Vκ8–220GL gene (24), and the Jκ2 segment (21). The Vκ consensus sequence of VI20L and VI22L (VκVI20/22) is identical to an unrelated Vκ sequence (accession no. AF045518) and presumably represents a previously undescribed germ-line gene of the Vκ21 family. The sequence data are available from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory nucleotide sequence database (accession nos. AJ400966–81).