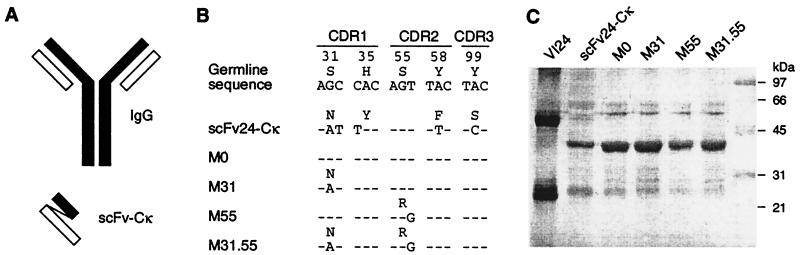
Figure 2.
Structural characteristics of the IgG VI24 and of recombinant scFv-Cκ. (A) Schematic diagram of a prototypical IgG (heavy chain, black; light chain, white) and of recombinant scFv-Cκ. In scFv-Cκ the carboxyl terminus of the VH domain (black) is linked via the 18-aa linker [VE(GGS)4GGVD] to the amino terminus of the κ light chain, consisting of the Vκ and the Cκ domains (white). (B) Sequence alignment of scFv24-Cκ derived from the parental antibody VI24 and of the scFv-Cκ derivatives M0, M31, M55, and M31.55. With the exception of the shown VH codons 31, 35, 55, 58, and 99, sequences were identical (for notation and numbering see the legend of Fig. 1). The sequence data are available from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory nucleotide sequence database (accession nos. AJ400982–6). (C) SDS/PAGE analysis of purified VI24 and of purified scFv-Cκ proteins. Four micrograms of purified protein was separated by SDS/12% PAGE under reducing conditions and was visualized by silver staining (Bio-Rad). The IgG2a antibody VI24 gave rise to two bands, at 50 kDa for the heavy chain and at 25 kDa for the light chain. In contrast, the different scFv-Cκ proteins showed one major band at approximately 38 kDa, verifying the single-chain character of the proteins. In the last lane a prestained low-molecular-mass protein standard (Bio-Rad) was run.