Figure 1.
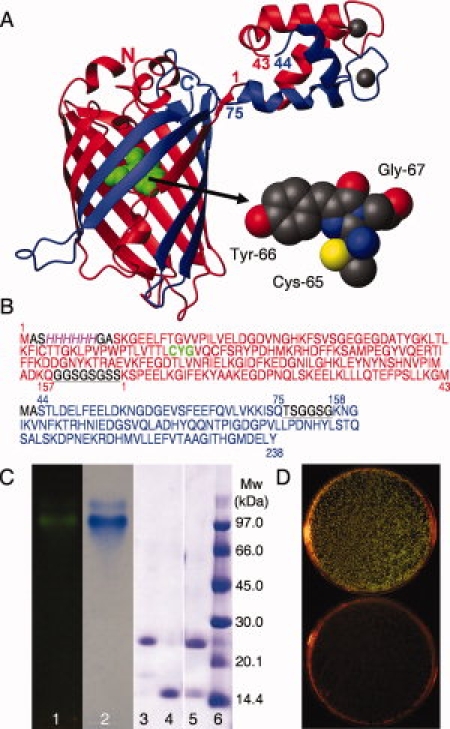
A, left) Cartoon of EF1 and EF2 from calbindin D9k fused to the N- and C-terminal fragments of GFP. The N-terminal fragment is shown in red and the C-terminal fragment in blue, with the N- and C-termini of GFP marked by letters, and the first and last residue of each EF-hand partner marked with numbers. The chromophore is shown in green. A, right) The chromophore formed by a covalent reaction between residues Cys 65, Tyr 66 and Gly 67 is shown in a space filling model. The figure was prepared using MOLMOL20 and the pdb files 1EMA and 4ICB. B): Amino acid sequences of the fragments forming the reconstituted protein. GFP-N (res. 1–157) and EF1 of calbindin D9k (res. 1–43) are red and the chromophore marked in green, EF2 of calbindin D9k (res. 44–75) and GFP-C (res. 158–238) are blue. The 6xHis-tag is also indicated (italic, magenta) and the linker regions between the fragments are black and underlined. C) Gel electrophoresis of the GFPN-EF1·EF2-GFPC complex and fragments. Lane 1: Agarose gel of GFPN-EF1·EF2-GFPC complex before coomassie staining visualized using a Dark Reader DR45M transilluminator. Lane2: Agarose gel of GFPN-EF1·EF2-GFPC complex after coomassie staining. Lanes 3–6: SDS-PAGE; 3: GFPN-EF1, 4: EF2-GFPC, 5: GFPN-EF1·EF2-GFPC complex, 6: Molecular weight standard. D) Co-transformation of the plasmids coding for GFPN-EF1 and EF2-GFPC give green colonies when spread on inducing media, plate B, (top) but not when spread on media containing only the antibiotics, plate A (bottom).
