Figure 1.
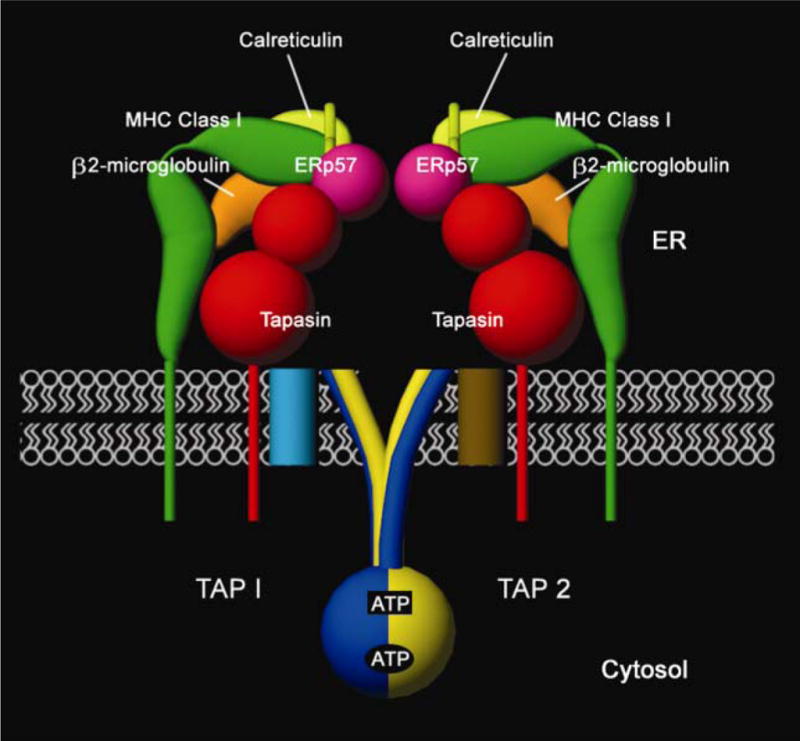
Components of the peptide-loading complex in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I heavy chains (green) and β2m (orange) are found in association with tapasin (red) and the TAP1-TAP2 (blue and yellow, respectively) complex. Many generic ER factors are also found in association with TAP, tapasin and MHC class I, including calreticulin (light green), ERp57 (purple) and PDI (not shown), which together constitute a complex called the PLC [1]. This complex forms an intricate molecular machine that recruits peptide-deficient heterodimers of heavy chains and β2m, transports peptide cargo from the cytosol to the ER, facilitates assembly of peptide with MHC class I heterodimers and ensures appropriate release of peptide-loaded MHC class I molecules. TAP1 and TAP2 each contain a cytosolic NBD and a transmembrane region with multiple membrane-spanning segments. The N-terminal region of the TAP transmembrane domain (light blue and brown cylinders in the membrane) forms a separate tapasin binding domain of the TAP complex [5–7]. The cytosolic face of TAP1-TAP2 complexes depicts the predicted closed-state NBD dimer [9,10]. Two ATP molecules are sandwiched at the NBD dimer interface; between the Walker A region of TAP1 NBD and the signature motif of TAP2 NBD (lower oval-shaped site, TAP1 site) and between the Walker A region of TAP2 NBD and the signature motif of TAP1 NBD (upper rectangular site, TAP2 site). The TAP2 site is the main catalytic site driving peptide transport [10–13]. The figure depicts a hypothetical scheme of interactions between the luminal domains of tapasin, ERp57, calreticulin and MHC class I, and the precise nature of the interactions remains to be defined. Only the tapasin-binding domain of ERp57 is depicted. ER, endoplasmic reticulum; ERp57, ER oxidoreductase of 57 KDa; NBD, nucleotide binding domain; PDI, protein disulfide isomerase; PLC, peptide loading complex; TAP, transporter associated with antigen processing.
