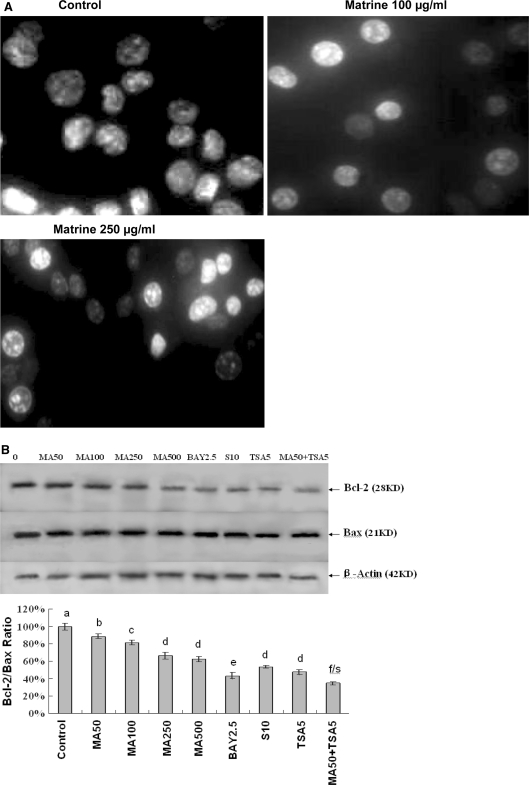
Fig. 3.
In vitro effects of matrine on induction of apoptosis (A) and reduction of Bcl-2/Bax protein ratio (B) in A549 cells by matrine with its synergistic anticancer agent trichostatin A. A Induction of apoptosis in A549 cells by treatment for 48 h with matrine at concentrations of 0 (0.1% DMSO vehicle as the control), 100 and 250 μg/mL. The treated cells were stained with Hoechst 33258 and the apoptotic morphological changes in the nuclear chromatin were observed under a fluorescent microscope as described in the “Materials and methods” section. B Reduction of Bcl-2/Bax protein ratio in A549 cells by treatment for 48 h with matrine at the concentrations of 50–500 μg/mL (MA50, MA100, MA250, and MA500) in the absence or presence of Bay at 2.5 μM (BAY2.5, the inhibitor of NF-κB), celecoxib at 10 μM (S10, the inhibitor of cyclooxygenase-2), and trichostatin A at 5 μg/L (TSA5). The protein expressions of Bcl-2 and Bax were analyzed by Western blotting as described in the “Materials and methods” section. Anti-β-Actin antibody was used as a sample loading control. The ratio of Bcl-2 and Bax, (the ratio of relative density of each band normalized to β-actin), shown as mean ± SD (Bar) is relative to that of 0 (0.1% DMSO vehicle) as the control (designated as 100%). For one experiment, 3 assays were carried out and only one set of gels is shown. Comparison was made by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test to establish whether significant differences existed between the groups. Values with different letters (a–f) differ significantly (P < 0.05); f/s represents the significant synergistic effect (P < 0.05) compared with the treatment with its individual compound alone. Statistically significant synergistic effect on the Bcl-2/Bax ratio was observed in A549 cells treated with MA50 + TSA5 compared with the individual MA50 or TSA5 treatment alone (P < 0.001, two-way ANOVA)