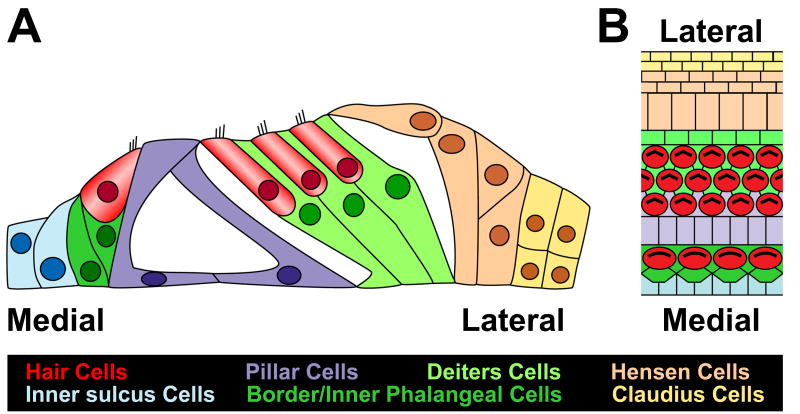
Figure 1. Anatomy of the organ of Corti.
Cross-sectional (A) and lumenal surface (B) illustrations of the cellular anatomy of the organ of Corti. Medial and lateral sides are labeled for orientation. A single row of inner hair cells (red) is located on the medial side of the epithelium, while three rows of outer hair cells (red) are located more laterally. Inner hair cells are separated from one another by border cells and inner phalangeal cells (dark green), while outer hair cells are separated by Deiters cells (light green). The inner and outer hair cell regions are separated by the tunnel of Corti, a fluid filled structure that is bounded by single rows of inner and outer pillar cells (purple). Hensen and Claudius cells (beige, yellow) are located at the lateral edge.