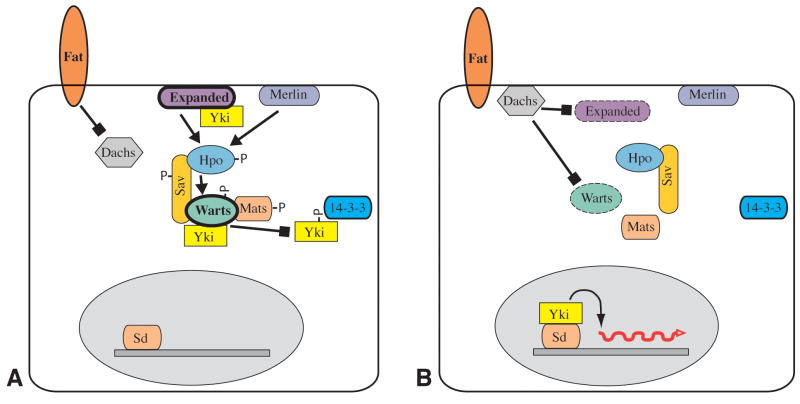
Fig 5. Model of Yki regulation.
A) In the Yki “off” state, Wts is active, and levels of Wts and Ex are high (thick outline). Active Warts phosphorylates Yki, which inhibits Yki by promoting its association with 14-3-3 proteins in the cytoplasm, thereby excluding it from the nucleus. In addition, Wts and Ex can directly bind Yki to exclude it from the nucleus B) In the Yki “on” state, Wts is inactive, and levels of Wts and/or Ex are lower (dashed outline). Components of the Hippo kinase cassette are unphosphorylated, and interactions between them are reduced. Yki is not phosphorylated, and enters the nucleus where it complexes with Sd to promote the transcription of downstream target genes.