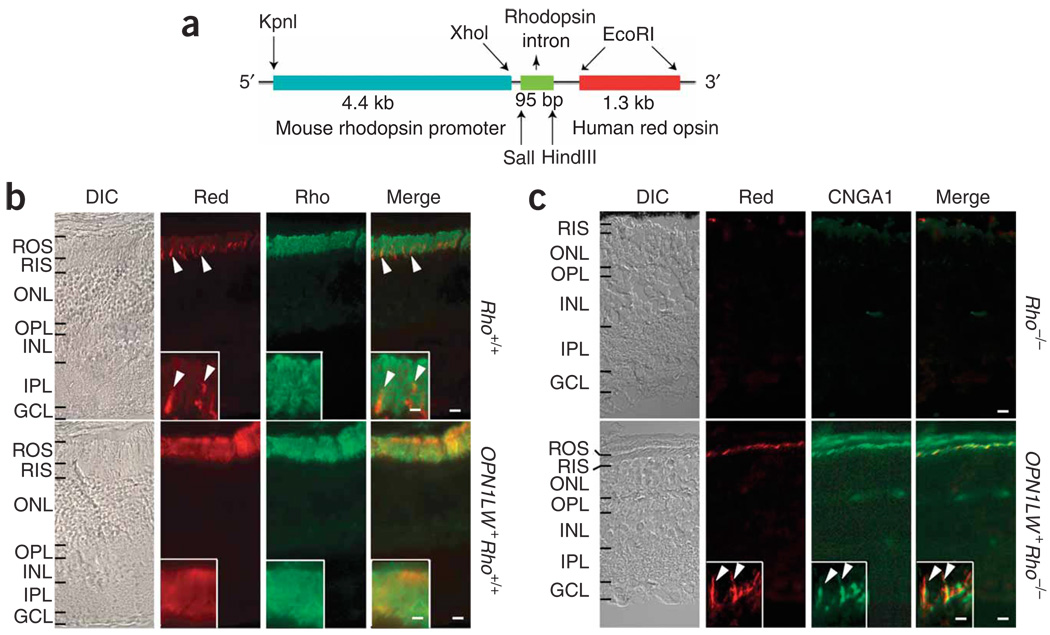
Figure 1.
Mouse rods expressing transgenic human red cone pigment. (a) Transgene construct. The 4.4-kb mouse rhodopsin promoter fragment was linked to a 1.3-kb cDNA coding for human red cone opsin. The third intron of the human rhodopsin gene was inserted between the two to improve expression. (b) Frozen sections from Rho+/+ (wild type) and OPN1LW+ Rho+/+ (transgenic) mouse retinas immunostained for red cone pigment (red) and rhodopsin (rho). Arrowheads, sporadic mouse cones (presumably green cones) in Rho+/+ retina cross-labeled by the antibody. Inset, high-magnification view of outer segment layer. DIC, differential interference contrast. (c) Frozen sections from 2-month-old Rho−/− and OPN1LW+ Rho−/− (transgenic without rhodopsin) mouse retinas immunostained for red cone pigment and rod marker CNGA1. Note the absence of an outer segment layer in Rho−/− retina and its presence, although it is thin, in OPN1LW+ Rho−/− retina. Inset, high-magnification view of OPN1LW+Rho−/− rod outer segments with red cone pigment (arrowheads). ROS, rod outer segment; RIS, rod inner segment; ONL, outer nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer. Scale bars: 10 µm in main panels, 2 µm in insets.