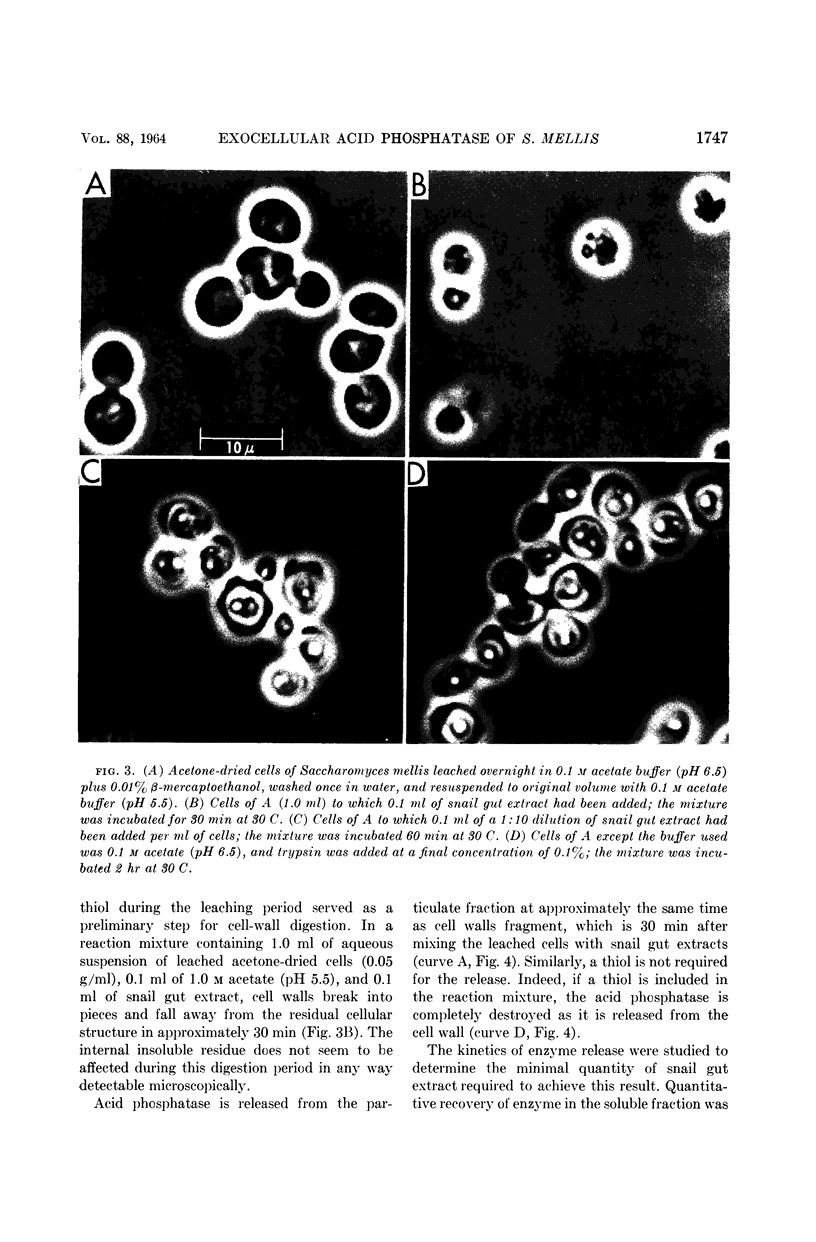
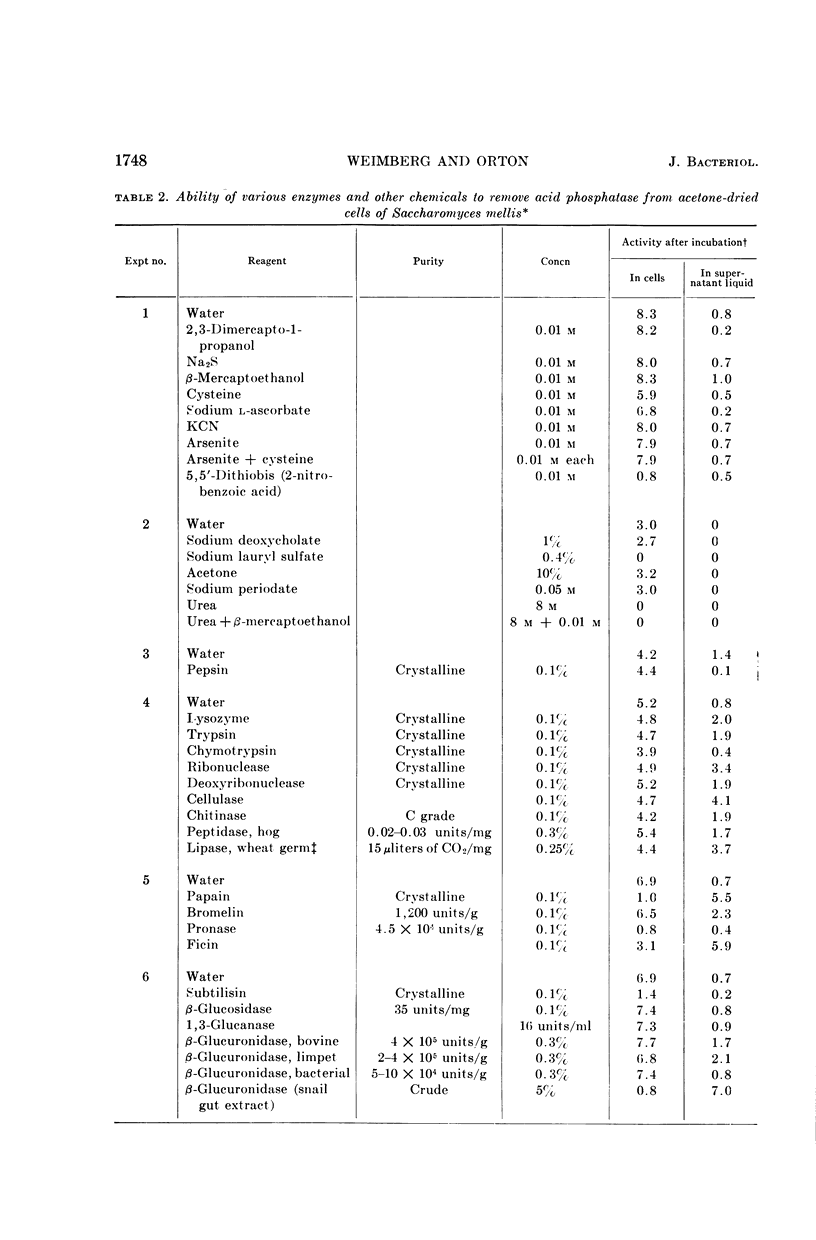
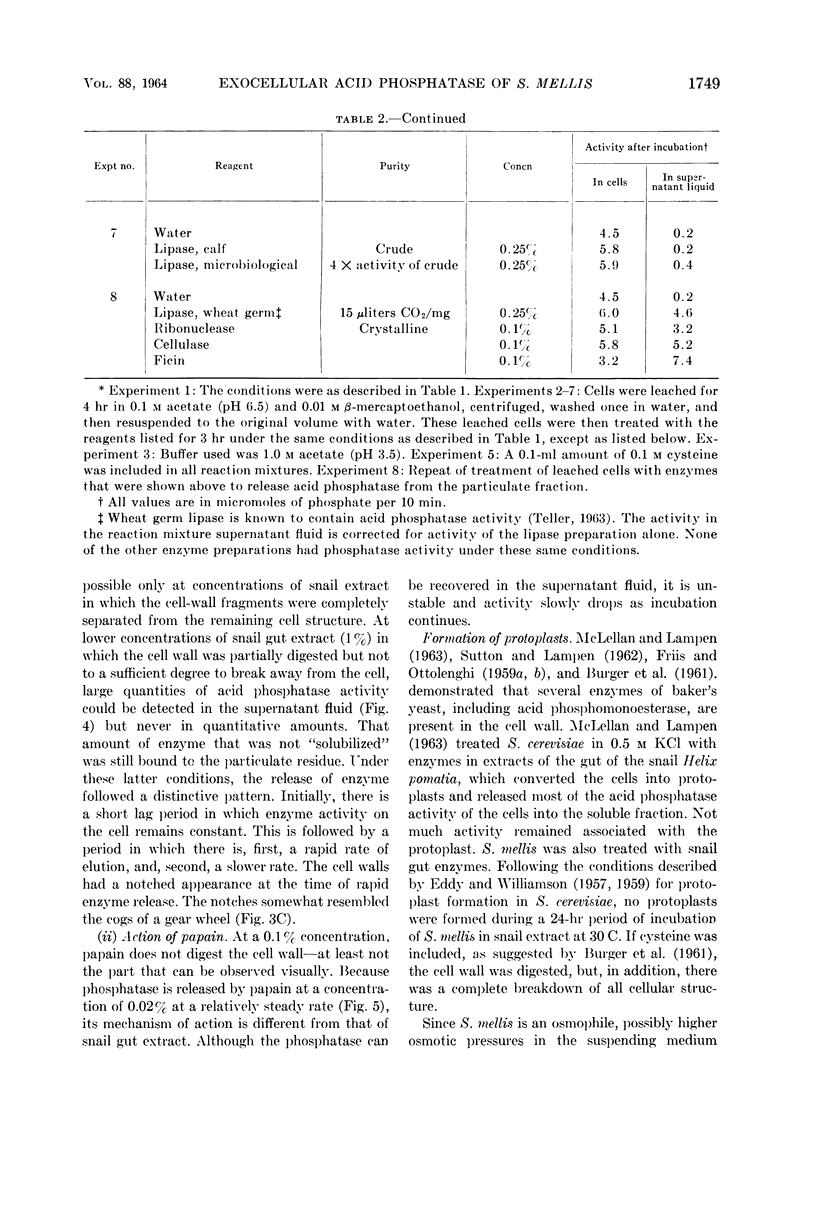
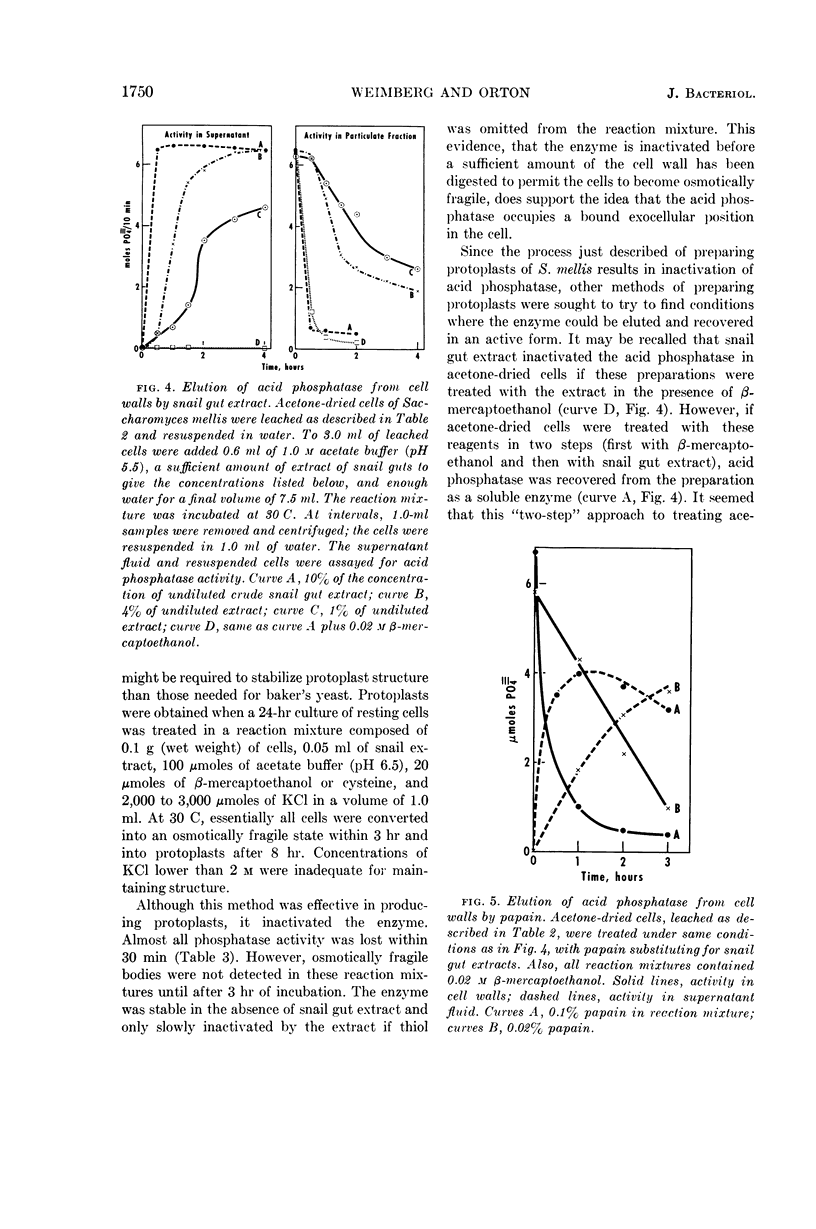
Abstract
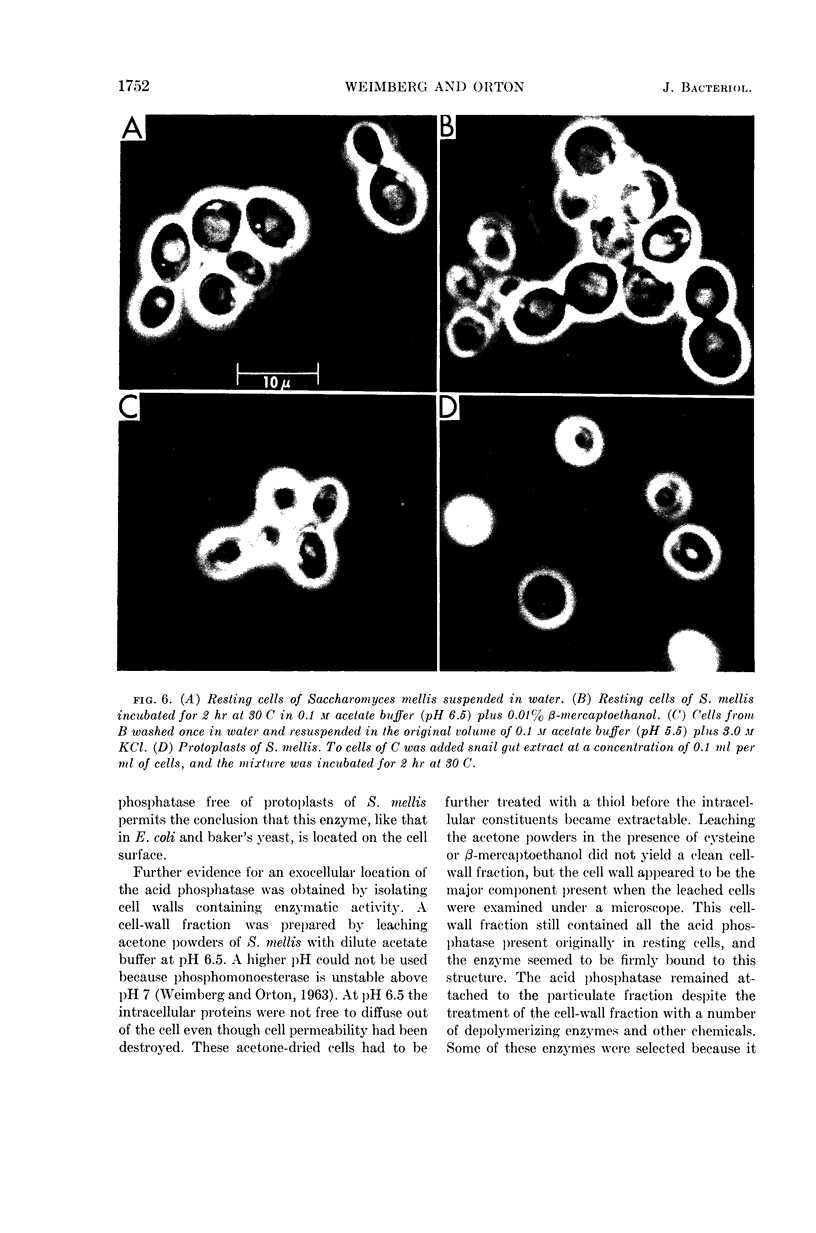
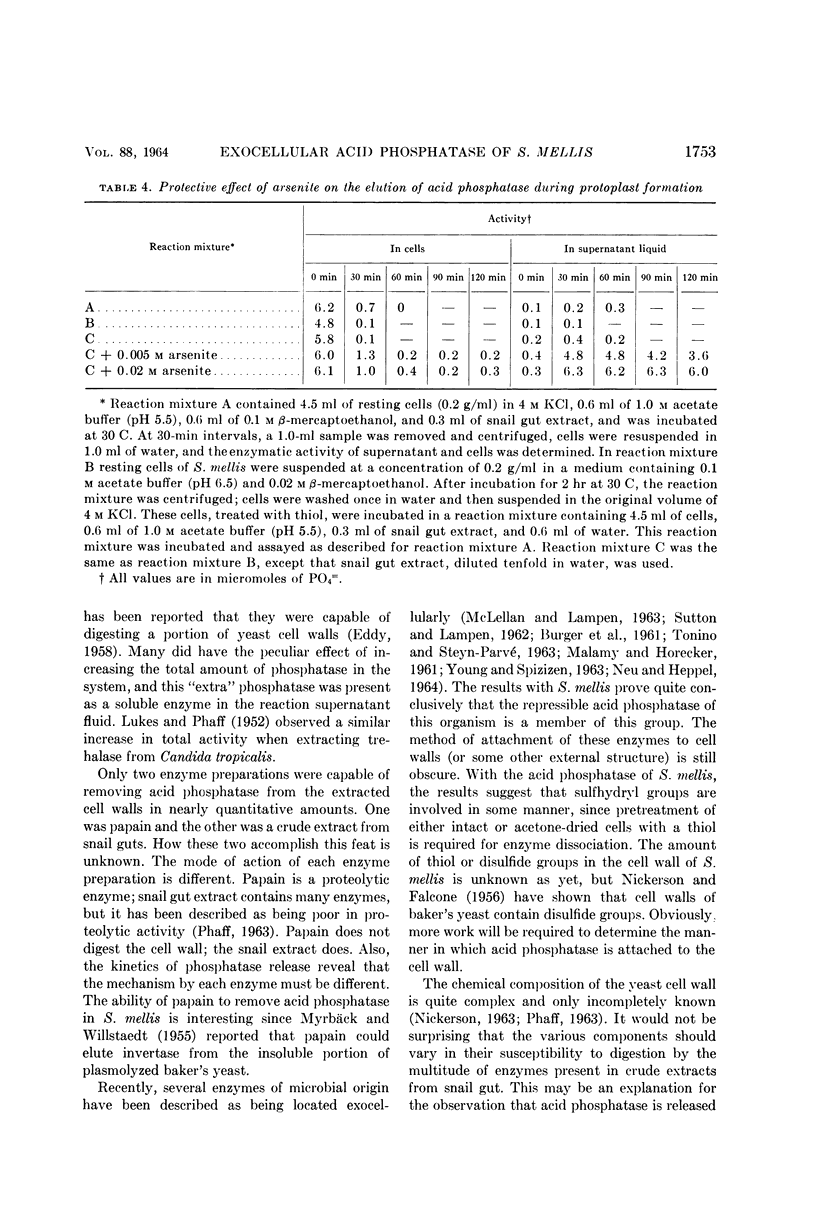
Weimberg, Ralph (Northern Regional Research Laboratory, Peoria, Ill.), and William L. Orton. Evidence for an exocellular site for the acid phosphatase of Saccharomyces mellis. J. Bacteriol. 88:1743–1754. 1964.—Evidence is presented which demonstrates an exocellular location for acid phosphatase in Saccharomyces mellis. Derepressed intact cells exhibit acid phosphatase activity. The properties of the system are similar to those shown by the enzyme in cell-free extracts. There is no increase in total activity when cell-free extracts are prepared. Enzymatically active cell walls were prepared by leaching acetone-dried cells of this yeast in dilute acetate buffer (pH 6.5) plus β-mercaptoethanol. The insoluble residue, consisting mainly of cell-wall material and containing the phosphatase, was treated with a variety of hydrolytic enzymes and other chemicals. Only papain and crude snail gut extracts dissociated the enzyme from the particulate fraction in nearly quantitative amounts. The mechanism of release by these two enzymes probably differs. Of all enzymes tested, only the snail gut extract digested the cell walls. By dividing the procedure for making protoplasts of S. mellis into two steps, acid phosphatase may be dissociated from resting cells and recovered as an active soluble enzyme. The first step is to pretreat the cells with a thiol reagent. The second step is to digest the cell wall by enzymes present in crude snail gut extracts. Arsenite must be included in the second step to protect the phosphatase from inactivation. The phosphatase is quantitatively released before the cell becomes osmotically fragile.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURGER M., BACON E. E., BACON J. S. Some observations on the form and location of invertase in the yeast cell. Biochem J. 1961 Mar;78:504–511. doi: 10.1042/bj0780504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDDY A. A., WILLIAMSON D. H. Formation of aberrant cell walls and of spores by the growing yeast protoplast. Nature. 1959 Apr 18;183(4668):1101–1104. doi: 10.1038/1831101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDDY A. A. [The structure of the yeast cell wall. II. Degradative studies with enzymes]. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1958 Dec 17;149(936):425–440. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1958.0085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALCONE G., NICKERSON W. J. Identification of protein disulfide reductase as a cellular division enzyme in yeasts. Science. 1956 Oct 19;124(3225):722–723. doi: 10.1126/science.124.3225.722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIIS J., OTTOLENGHI P. Localization of invertase in a strain of veast. C R Trav Lab Carlsberg. 1959;31:259–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIIS J., OTTOLENGHI P. Localization of melibiase in a strain of veast. C R Trav Lab Carlsberg. 1959;31:272–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUKES T. M., PHAFF H. J. Characteristics of trehalase in Candida tropicalis. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1952;18(4):323–335. doi: 10.1007/BF02538620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALAMY M., HORECKER B. L. The localization of alkaline phosphatase in E. coli K12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1961 Jun 2;5:104–108. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(61)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCLELLAN W. L., Jr, LAMPEN J. O. The acid phosphatase of yeast. Localization and secretion by protoplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Feb 12;67:324–326. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91832-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICKERSON W. J. SYMPOSIUM ON BIOCHEMICAL BASES OF MORPHOGENESIS IN FUNGI. IV. MOLECULAR BASES OF FORM IN YEASTS. Bacteriol Rev. 1963 Sep;27:305–324. doi: 10.1128/br.27.3.305-324.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. The release of ribonuclease into the medium when E. coli cells are converted to spheroplasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964;14:109–112. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90238-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHAFF H. J. CELL WALL OF YEASTS. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1963;17:15–30. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.17.100163.000311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT G., BARTSCH G., LAUMONT M. C., HERMAN T., LISS M. Acid phosphatase of bakers' yeast: an enzyme of the external cell surface. Biochemistry. 1963 Jan-Feb;2:126–131. doi: 10.1021/bi00901a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUOMALAINEN H., LINKO M., OURA E. Changes in the phosphatase activity of Baker's yeast during the growth phase and location of the phosphatases in the yeast cell. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jan 29;37:482–490. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90505-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTTON D. D., LAMPEN J. O. Localization of sucrose and maltose fermenting systems in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jan 29;56:303–312. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90567-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAUSSKY H. H., SHORR E. A microcolorimetric method for the determination of inorganic phosphorus. J Biol Chem. 1953 Jun;202(2):675–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TONINO G. J., STEYN-PARVE E. P. Localization of some phosphatases in yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Mar 12;67:453–469. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91851-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
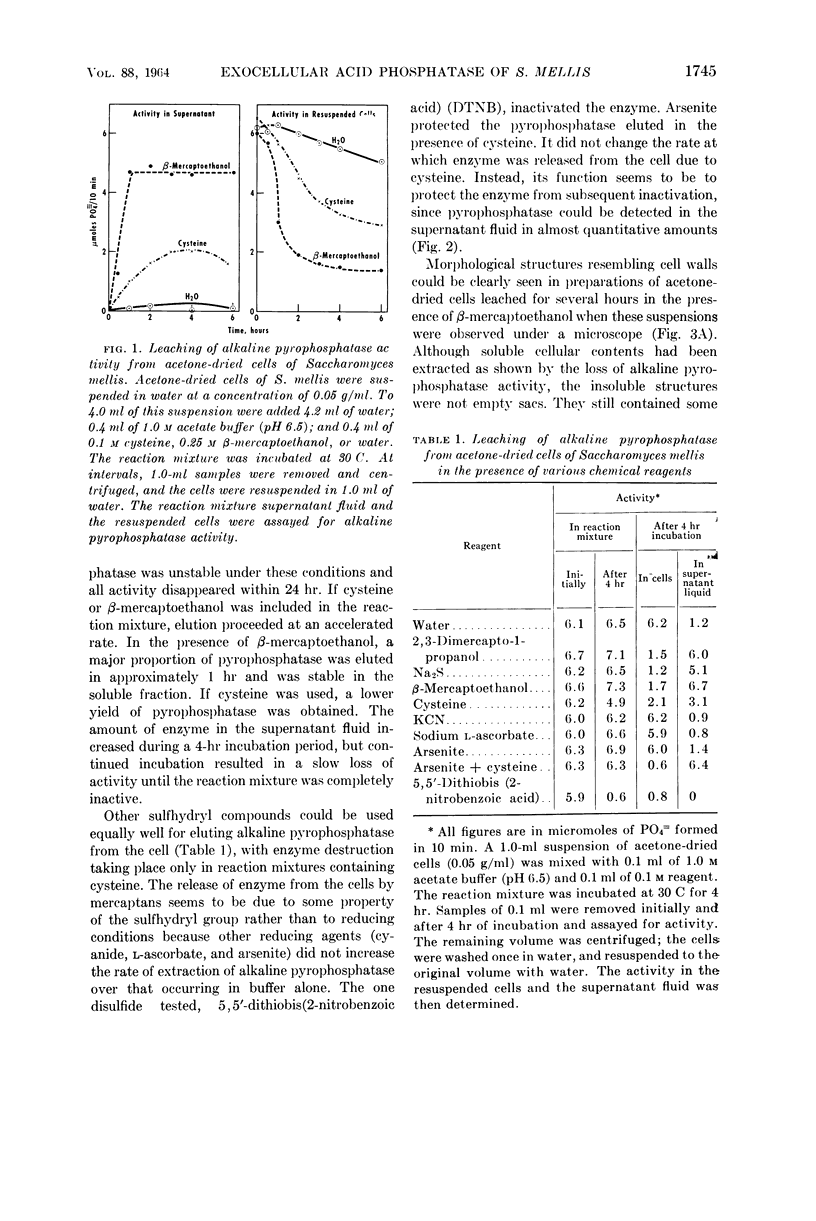
- WEIMBERG R., ORTON W. L. REPRESSIBLE ACID PHOSPHOMONOESTERASE AND CONSTITUTIVE PYROPHOSPHATASE OF SACCHAROMYCES MELLIS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:805–813. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.4.805-813.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
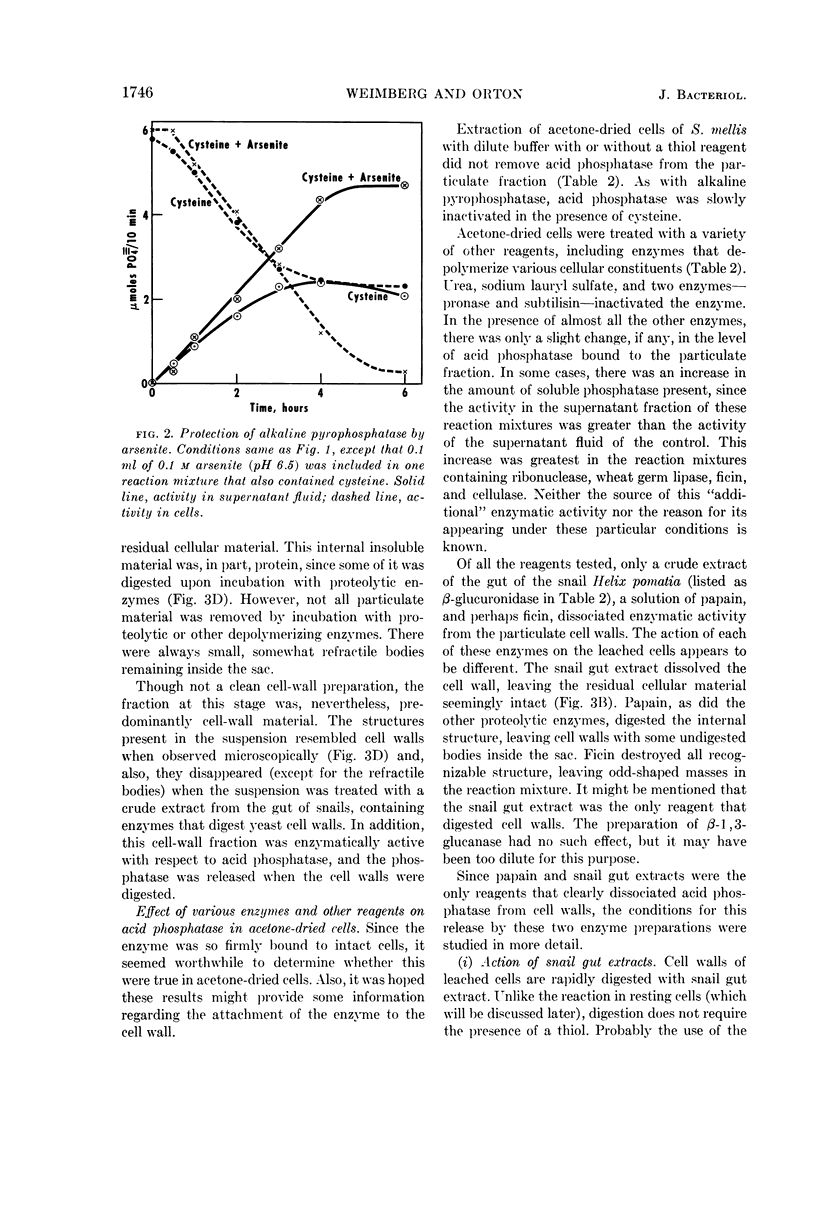
- YOUNG F. E., SPIZIZEN J. BIOCHEMICAL ASPECTS OF COMPETENCE IN THE BACILLUS SUBTILIS TRANSFORMATION SYSTEM. II. AUTOLYTIC ENZYME ACTIVITY OF CELL WALLS. J Biol Chem. 1963 Sep;238:3126–3130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]