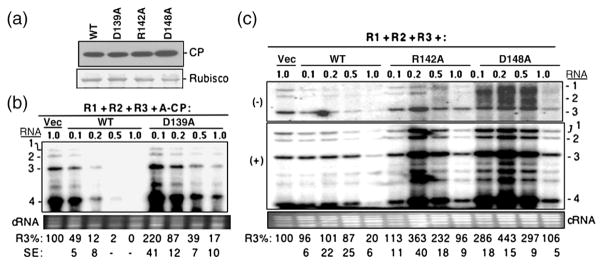
Fig. 4.
Characterization of the three BMV CP mutants that affected the ability to repress RNA accumulation. (a) Western blot of CP expression level in N. benthamiana plants infiltrated with Agrobacterium (OD595 of 1.0) harboring the empty vector or pCP that can express either WT or mutant BMV CP. The entire leaf was macerated and clarified by centrifugation at 13,000g, and then an aliquot was subjected to SDS-PAGE and transferred onto PVDF membrane. The primary antibody was rabbit anti-CP polyclonal antibody. A Coomassie blue-stained small subunit of Rubisco was used as the protein loading control. The mean and standard error values of at least three independently assayed samples are shown below the gel image. (b) Titration of Agrobacterium expressing CP mutant D139A on BMV RNA accumulation. N. benthamiana plants were infiltrated with a mixture of Agrobacterium expressing three genomic RNAs (each at an OD595 of 0.1) along with culture that can express either WT CP or the D139A mutant at the concentrations noted above the gel image. Viral RNA was detected by a Northern blot assay, and RNA3 was quantified at the bottom of the image as a percentage of the vector control. The standard error values represent one standard deviation from at least three independently assayed samples. Those dented with a dash were deemed to be below the limit of accurate detection by phosphorimage analysis. (c) Effects of titration of Agrobacterium expressing CP mutants R142A and D148A on RNA accumulation. The minus-strand (top panel) and plus-strand (middle panel) RNAs were detected by Northern blot with specific probe. The bottom panel contains ethidium-bromide-stained cellular RNA used as a loading control. Quantification of the plus-strand BMV RNAs is shown at the bottom of the gel image and is representative of two independent experiments with four independent samples.