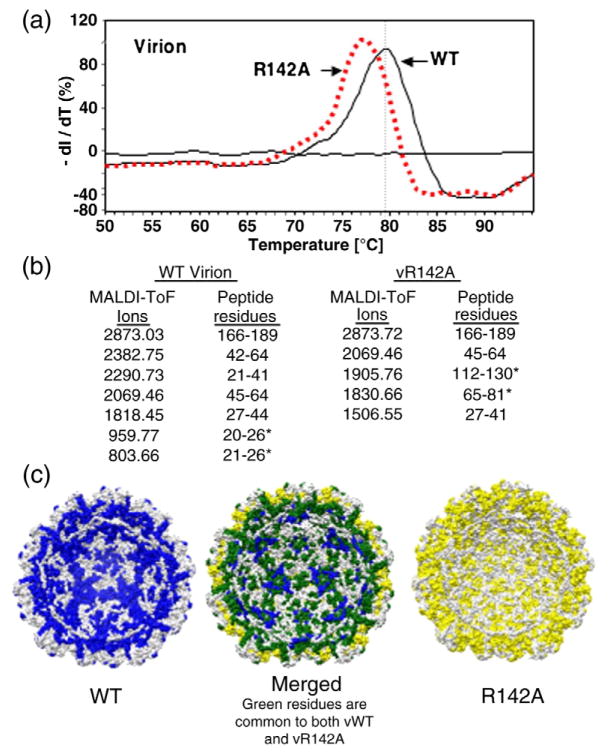
Fig. 8.
Biophysical characterization of the R142A virion. (a) Differential scanning fluorimetry to determine the Tm values of WT and R142A virions. The experiment was performed in an Eppendorf Master-cycler EP Realplex machine with SYPRO orange as the molecular probe. The 96-well plate containing all the samples was heated at a rate of 1.0 °C/min, from 25 to 95 °C, and the fluorescence intensity was measured with excitation/emission wavelengths of 470/550 nm. The Tm values were calculated by obtaining the maximum of the first derivative using KaleidaGraph. (b) MS of peptides that interact with viral RNA in WT and R142A virions. Data collection was performed on a Bruker Biflex III MALDI-ToF mass spectrometer. Samples were desalted using a ZipTip and spotted on the sample plate in α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid matrix (mass=189.17 Da). Positive ions from masses 400–4000 Da were analyzed in reflectron mode. The MS data are shown in Supplementary Fig. 2. (c) A molecular model of the RNA-contacting residues within the inner cavity of the R142A mutant virion (maize), the WT virion (blue), and the merged models that show the differences in the RNA contacts (spartan green).